Figure 6.
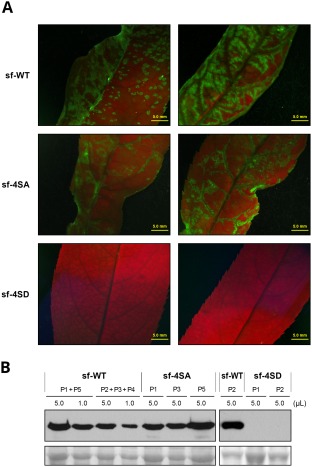
Infection in Prunus persica by wild‐type Plum pox virus (PPV) (sf‐WT) and PPV mutants carrying changes that prevent (sf‐4SA) or mimic (sf‐4SD) capsid protein (CP) phosphorylation at serine residues 25, 81, 101 and 118. P. persica seedlings were inoculated by bombardment with viral cDNA. (A) Images of upper uninoculated leaves of plants infected with the indicated viruses, at 21 days post‐inoculation (dpi), under an epifluorescence microscope. Bar, 5 mm. (B) PPV CP‐specific immunoblot analysis of extracts from upper uninoculated leaves for individual or pooled plants, collected at 21 dpi. Viruses used as inocula and volume of extract loaded are indicated. Blots stained with Ponceau red showing the ribulose‐1,5‐bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) protein are included as loading control.
