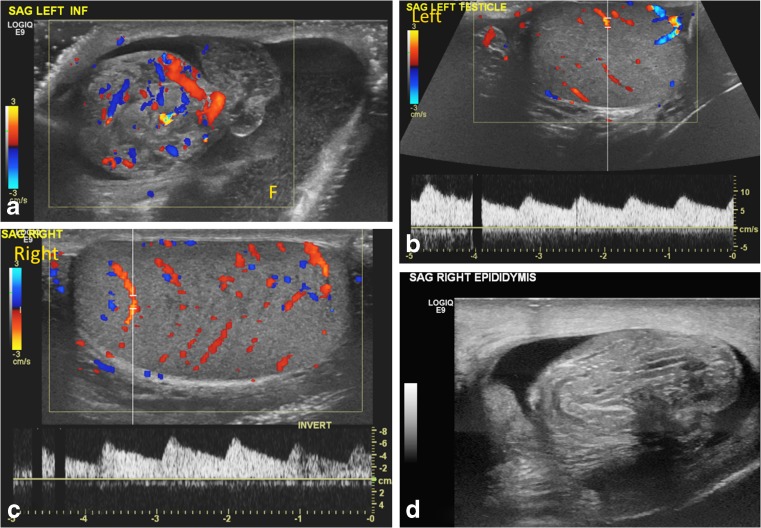
Fig. 11.
Bilateral partial torsion in a 15-year-old boy who presented with acute left testicular pain. a Color Doppler US image of the upper left scrotal sac shows an enlarged epididymal-cord complex with flow within, and surrounding complex hydrocele with mobile echoes. b, c Preserved slightly asymmetrical — left (b) less than right (c) — intratesticular flow and symmetrical waveforms are appreciated. The enlarged epididymal-cord complex was confused for epididymitis. d Follow-up exam after 4 months for recurrent testicular pain, now on the right side, shows an enlarged epididymal-cord complex in the right scrotum. Bilateral partial torsion (270° twist on the right side and 90° twist on the left side) and bilateral bell clapper anomaly were detected at orchiopexy