Figure 2.
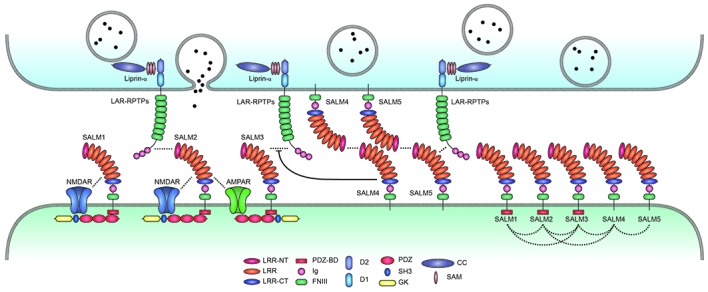
Trans-synaptic, cis-, and cytoplasmic interactions of SALMs. SALMs interact trans-synaptically with presynaptic LAR-RPTPs (LAR, PTPσ and PTPδ), in cis with AMPA/NMDA receptors and other SALM proteins, and cytoplasmically with the postsynaptic scaffolding protein PSD-95 (in the case of SALMs 1–3 but not SALM4 or SALM5). Protein interactions are indicated by the close proximity of the indicated proteins/domains or by dotted lines. Whether SALMs directly interact with NMDA/AMPA receptors remains to be determined. The trans-synaptic interactions between postsynaptic SALM3/5 and presynaptic LAR-RPTPs are known to promote presynaptic differentiation, although the function of the newly identified SALM2–LAR-RPTP (PTPδ) interaction is unclear. SALM4 interacts in cis with SALM3 to suppress the binding of SALM3 to presynaptic LAR-RPTPs and SALM3-dependent presynaptic differentiation. Postsynaptic SALM5 can also interacts with presynaptic SALM5 in a homophilic manner, which may interfere with the trans-synaptic interaction between presynaptic LAR-RPTPs and postsynaptic SALM5. The cis-interactions between different postsynaptic SALMs are based on both in vitro and in vivo results, and may be mediated by the SALM–SALM dimerization revealed by X-ray crystallographic studies. Although not shown here, some LAR-RPTPs are thought to be present and function at postsynaptic sites, in addition to presynaptic sites.
