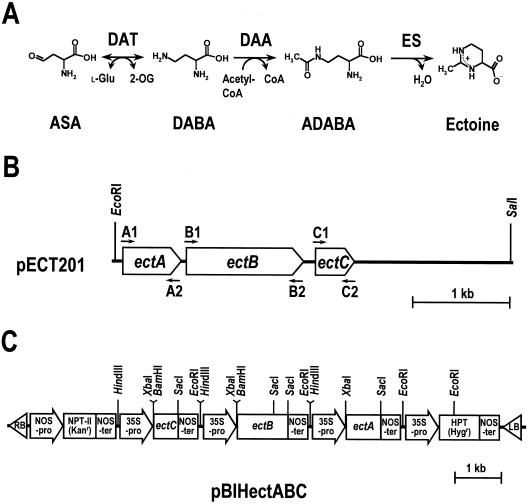
Figure 1.
H. elongata genes encoding the enzymes involved in ectoine synthesis introduced into BY2 cells. A, Ectoine biosynthetic pathway in H. elongata OUT30018. The first step is catalyzed by DAT, which converts ASA, an intermediate in amino acid metabolism, to l-2,4-diaminobutyric acid (DABA). The second step, which is the acetylation of DABA to Nγ-acetyl l-2,4-diaminobutyric acid (ADABA), is promoted by DAA. In the last step, ES catalyzes the cyclic condensation of l-2,4-diaminobutyric acid to yield tetrahydropyrimidine ectoine. B, Structure of the 4.1-kb DNA fragment containing the ect operon. ectA, ectB, and ectC genes encode DAA, DAT, and ES, respectively. The arrows show the approximate positions of the PCR primers used to amplify each ect gene. C, Structure of the plasmid pBIHectABC for expression of the ect genes in the transgenic BY2 cells. NPT-II, Neomycin phosphotransferase gene; Kanr, kanamycin-resistance gene; HPT, hygromycin phosphotransferase gene; Hygr, hygromycin-resistance gene; 35S-pro, 35S promoter of cauliflower mosaic virus; NOS-pro, nopaline synthase promoter; NOS-ter, nopaline synthase terminator; LB, left border; RB, right border.