Figure 1.
ILC1s Lack TRAIL Expression in NKp46-Deficient Mice
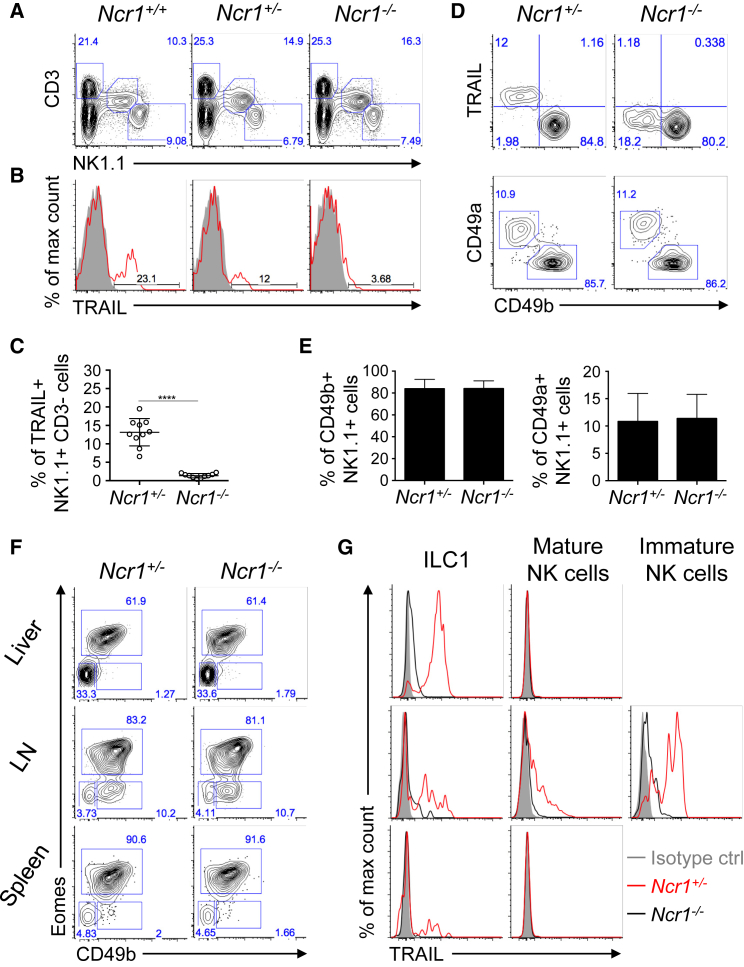
(A) Representative flow cytometry plots showing frequencies of T cells (CD3+ NK1.1−), NKT cells (CD3+ NK1.1+), and NK cells (CD3− NK1.1+) in the livers of naive wild-type mice, Ncr1−/− mice, or heterozygous Ncr1+/− mice.
(B and C) Representative flow cytometry histograms (B) and average percentage (± SD) (C) of TRAIL+ group1 ILCs detected in the livers of Ncr1+/− and Ncr1−/− mice.
(D and E) Representative flow cytometry plots of TRAIL, CD49b/DX5, and CD49a expression on hepatic group 1 innate lymphoid cells (CD3− NK1.1+) from naive Ncr1+/− and Ncr1−/− mice (D) and average percentage (± SD) of CD49b/DX5+ NK cells (E, left) and CD49a+ NK cells (E, right) as described in (D).
(F) Representative flow cytometry plots of the gating strategy used to distinguish (CD3− NK1.1+) ILC subsets: mature NK cells (CD49b+Eomes+) from immature NK cells (CD49b+Eomes−) and ILC1s (CD49b− Eomes−) in liver, lymph node (LN), and spleen tissues harvested from Ncr1+/− and Ncr1−/− mice.
(G) Representative flow cytometry histograms of TRAIL expression on the cell subsets defined in (F).
Data are representative of 2–4 experiments, each with 2–5 mice per group. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (unpaired t test).