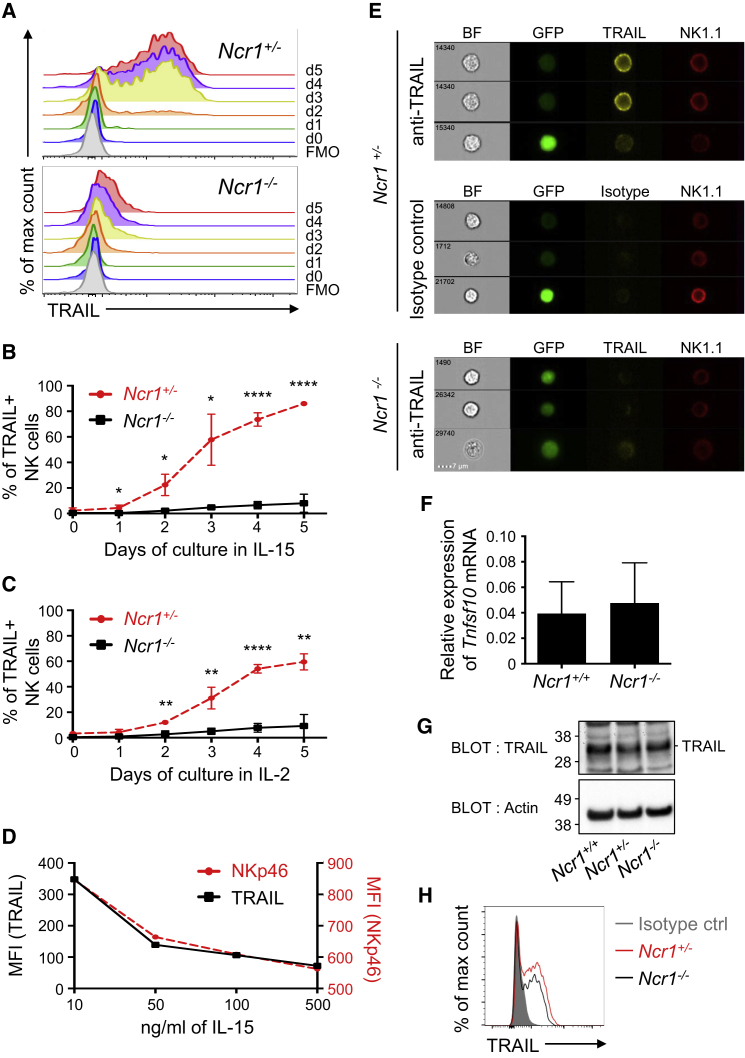
Figure 3.
IL-2 and IL-15 Fail to Induce TRAIL Protein Expression at the Membrane of NKp46-Deficient NK Cells
(A) Representative flow histograms of TRAIL induction on IL-15-activated splenic NK cells (CD3− NK1.1+) isolated from Ncr1+/− (top) and Ncr1−/− (bottom) mice (5 day culture in IL-15, 50 ng/mL). The negative control is depicted as fluorescence minus one (FMO).
(B and C) Average percentage (± SD) of TRAIL+ NK cells generated over 5 days of culture in the presence of IL-15 (50 ng/mL) (n = 3 mice/genotype) (B) and IL-2 (50 U/ml) (n = 3 mouse/genotype) (C). Values represent means ± SD. Statistical significance was measured via unpaired Mann-Whitney test).
(D) Mean fluorescence intensity of TRAIL and NKp46 co-expressed on splenic NK cells shown on day 5 for various concentrations of IL-15 as indicated in the plot.
The data in (A)–(D) are representative of 4 or more experiments.
(E) Representative confocal images obtained by ImageStream analysis of IL-15-activated NK cells isolated from Ncr1−/−(Ncr1gfp/gfp) and Ncr1+/−(Ncr1gfp/+) mice that express endogenous GFP. Staining with antibodies specific for NK1.1 and TRAIL or isotype phycoerythrin (PE) control is shown, as well as bright-field (BF) images. Zombie dye was used to gate out dead cells. Three cells representative of at least 480 events acquired (GFP+ NK cells) per condition are shown and are representative of 3 independent experiments. The scale bar represents 7 μm.
(F) Bar graph depicting the relative average expression (± SD) of Tnfsf10 mRNA in IL15-activated splenic NK cells isolated from Ncr1+/− and Ncr1−/− mice (5 days culture in IL-15, 50 ng/mL). Data are a pool of 3 mice per group combined from 1–2 experiments.
(G) Western blot analysis of the total TRAIL protein expressed in Ncr1+/+, Ncr1+/−, and Ncr1−/− NK cells upon activation (5 day culture in IL-2, 1,000 U/mL). Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. Actin was used as a reference.
(H) Representative flow histogram of TRAIL intracellular staining or isotype control (shaded gray) of IL-2-activated splenic NK cells isolated from Ncr1+/− (red line) and Ncr1−/− (black) mice.
Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. See also Figures S2 and S3.