Figure 2.
ZUFSP Is a Distinct Class of Deubiquitinating Enzymes
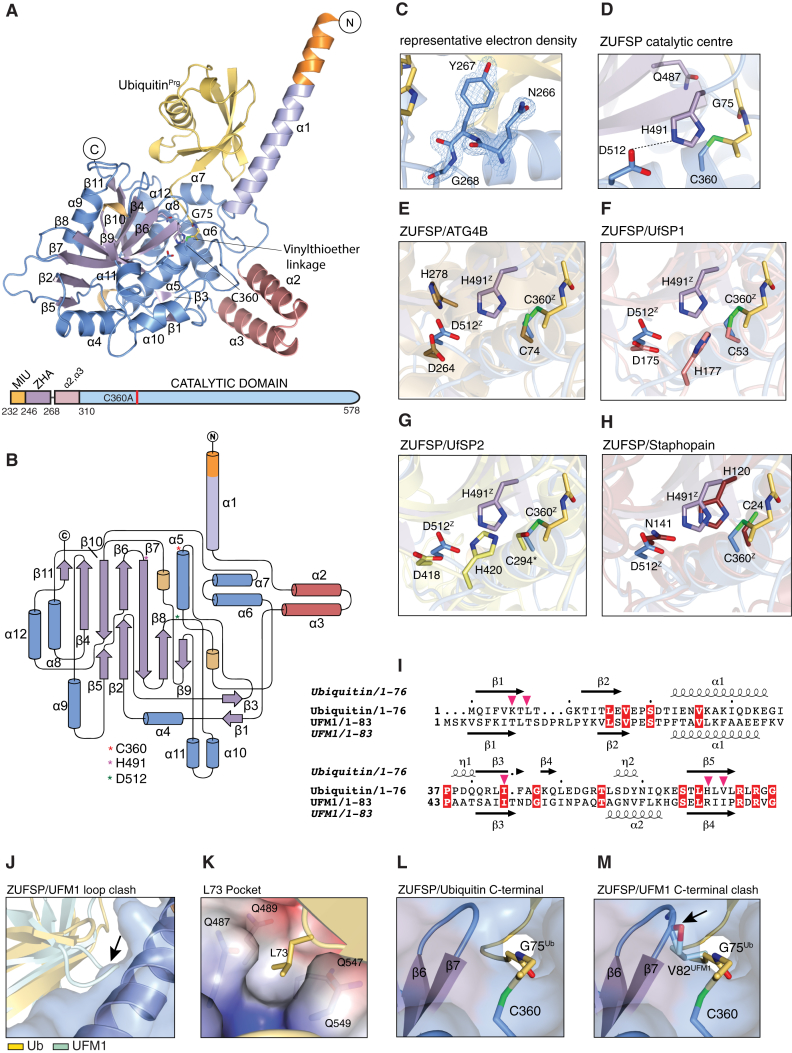
(A) Overall structure of the ZUFSP catalytic core domain. The secondary structural elements, α helix, β strand, and 3–10 helix, are highlighted in actinium blue, light purple, and light orange, respectively, with covalently bound Ub (yellow). The vinylthioether linkage connecting Ub with the catalytic cysteine of ZUFSP is shown in stick format. The catalytic core domain is connected to the helical arm indicated as ZHA (light blue) via a helix-loop-helix motif (salmon red, α2 and α3). The N terminus highlighted in orange is part of the MIU motif. Below: schematic representation of the ZUFSP 232–578 construct. Colors depicting the domains correspond to colors of the structure.
(B) Topology diagram showing ZUFSP architecture in 2D representation. The catalytic triad residues are indicated (asterisk).
(C) Representative electron density. 2Fo-Fc map of the residues corresponding to ZHA and the preceding loop contoured at 1σ.
(D) Close-up view highlighting catalytic triad residues C360, H491, and D512 and the oxyanion hole forming residue Q487.
(E–H) Close-up view of structure based alignments of ZUFSP with top matches based on the DALI server: Atg4b (PDB:2CY7) (E), UFSP1 (PDB: 2Z84) (F), UFSP2 (PDB: 3OQC) (G), and Staphopain (PDB:1CV8) (H).
(I) Structural alignment of Ub with UFM1. The secondary structure elements for both Ub and UFM1 are shown. The Ub residues interacting with ZHA are indicated in asterisks. Fully conserved residues are shaded in red.
(J) Steric clash of UFM1 β1-β2 loop with ZHA as seen from the structural alignment of UFM1 onto Ub
(K) Electrostatic surface potential based representation shows the hydrophobic pocket formed by the aliphatic portions of Q487, Q489, Q547, and Q549.
(L) The C terminus of Ub (yellow) in the narrow ZUFSP catalytic groove
(M) Structural superposition of UFM1 (light blue). Bulky V82 of UFM1 clashes with the β6-β7 loop in ZUFSP.
See also Figure S2.