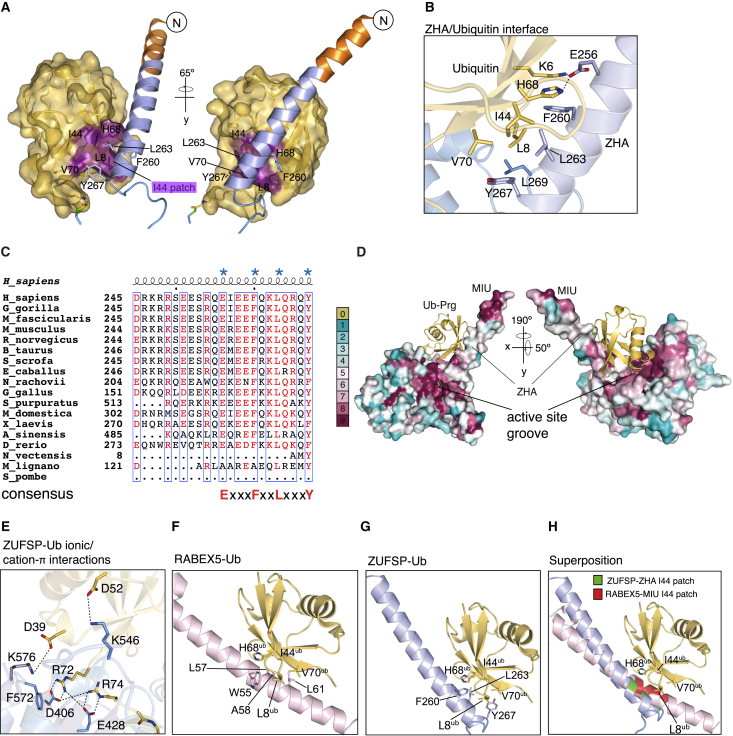
Figure 3.
ZUFSP Helical Arm Is a UBD
(A) ZHA-Ub interaction is predominantly hydrophobic. The interface shows the I44 patch (purple) on Ub (yellow) surface engaging with F260, L263, and Y267 residues of ZHA (cartoon representation, light blue).
(B) The network of interactions between ZHA and Ub, which include hydrophobic interactions, a salt bridge between K6 and E256 of ZHA and cation-π pair (K6-F260) is depicted.
(C) ZUFSP ZHA is conserved in evolution. Sequence alignment of ZHA from different organisms is shown. Secondary structure assignment is based on human ZUFSP. The ZHA residues interacting with Ub are highlighted with asterisks. Some species like N. vectensis and S. pombe altogether lack ZHA.
(D) Surface representation showing conserved residues on the surface of ZUFSP based on the sequence alignment in Figure S3 generated with the Consurf server (http://consurf.tau.ac.il). The residues around the catalytic center and Ub interacting ZHA patch are conserved through evolution.
(E) Interactions of distal Ub with ZUFSP. The Ub C-terminal residues R72 and R74 are involved in a network of ionic interactions with D406 and E428 of the catalytic domain.
(F) Structure of the MIU of RABEX5 (pink) in complex with Ub (yellow) (PDB: 2FIF) shown in cartoon representation.
(G) Structure of the ZHA of ZUFSP (blue) in complex with Ub (yellow) shown in cartoon representation.
(H) Comparison of MIU and ZHA interactions with Ub. Superposition of structures shown in (F) and (G) aligned on Ub.
See also Figure S3.