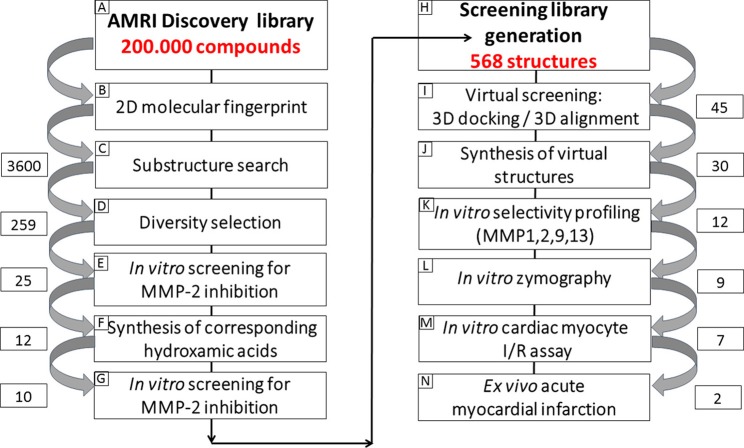
Figure 2.
The screening cascade. Complex screening cascade to identify candidates that may reduce acute cardiac I/R injury via inhibition of MMP-2. (A) AMRI Chemical Library contains ~200,000 drug-like small molecules (<500 Da) as compound set. We intended to select zinc-binding motif holding molecules, similar to hydroxamic acids. (B) For 2D substructure and similarity search. (C) Selection of free acids from the AMRI's compound's collection. (D) Further focus to compounds holding various motifs around a central core, reflecting the typical MMP inhibitor architecture. (E) Selected acids screened in a fluorescent assay using a recombinant human MMP-2 catalytic fragment and a synthetic peptide substrate. (F) The synthesis of the thiazole and the isosteric imidazole carboxylic acids. (G) The hydroxamic acid pairs of the previously measured acids were tested. (H) The novel thiazole carboxylic acid chemotype was the starting point for further structure-based optimization. A 568-membered focused library was in silico generated around the AMRI library hits including their bioisosters and some simplified analog. (I) Docking studies: Genetic Optimization for Ligand Docking (GOLD) was used to build a 3D model based on the X-ray structure of human MMP-2 and MMP-9. (J) Thirty compounds were successfully synthesized for screening combining the in silico hits and the additional designed compounds. (K) In vitro MMP-2 activity was measured using a fluorometric assay. (L) Low throughput screening by gelatin zymography technique. (M) Cell viability experiments in isolated neonatal cadiac myocytes subjected to simulated ischemia/reperfusion injury. (N) Myocardial infarct size was measured after ex vivo global ischemia experiments on isolated rat hearts.