Fig. 3.
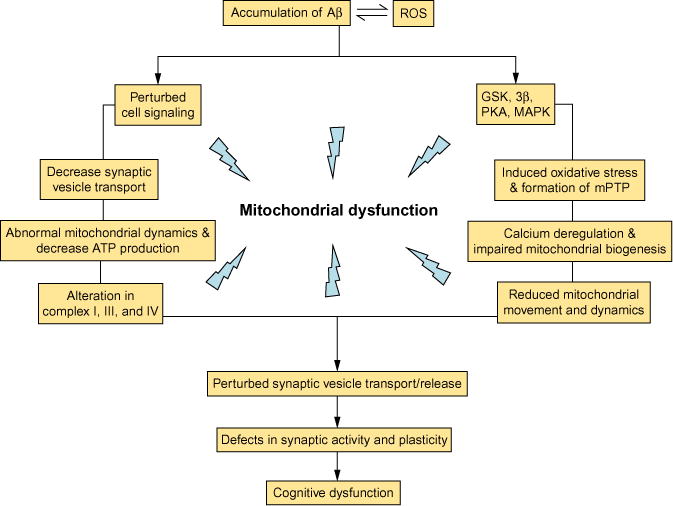
The cellular factors and related pathways contribute to Aβ-mediated mitochondrial defects and synaptic damage. Aβ accumulation perturbs mitochondrial transport and dynamics, cell signaling, synaptic mitochondrial structure and function, leading to decreased energy metabolism/ATP production, deregulation of calcium homeostasis, perturbed cell signaling cascades, altered key enzymes associated with mitochondrial respiratory chain, induced oxidative stress, and, eventually, synaptic injury and cognitive decline.
