Fig. 3.
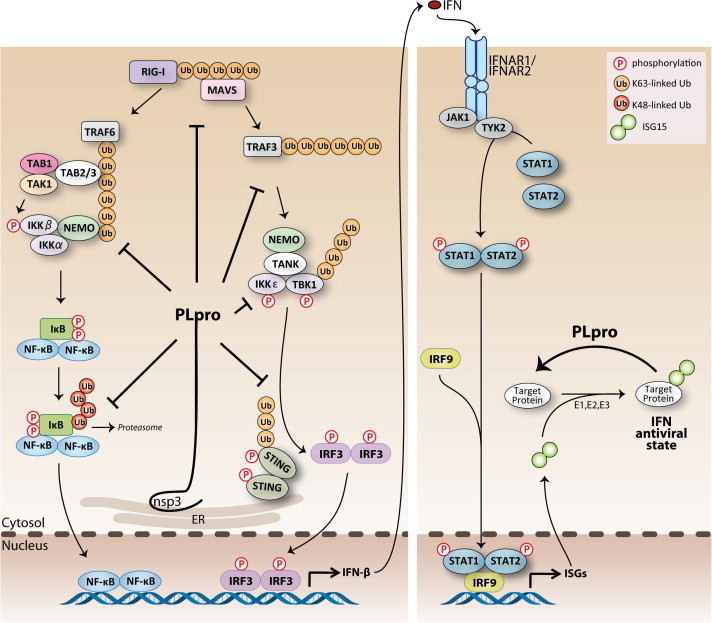
Currently proposed sites of action for SARS-CoV PLpro-mediated antagonism of the innate immune response. Viral infection is sensed by RIG-I (RIG-I-like helicase) and MDA-5 (melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5) recognition of viral RNA. Recruitment of adaptor proteins MAVS transduces signals to the downstream kinase complex, which activates the transcription factor, IRF-3 and NF-κB, which coordinates the expression of type I interferons (IFN-β and -α). Type I IFN induces the activation of STAT transcription factors resulting in the expression of ISGs (IFN-stimulated genes) and the establishment of an antiviral state in surrounding cells. PLpro can act on different branches of these pathways by interacting with or recognizing and deISGylating and/or deubiquitinating proteins within these pathways. The net effect of these different functions is to help SARS-CoV evade the host antiviral response via antagonizing the establishment of an antiviral state.
