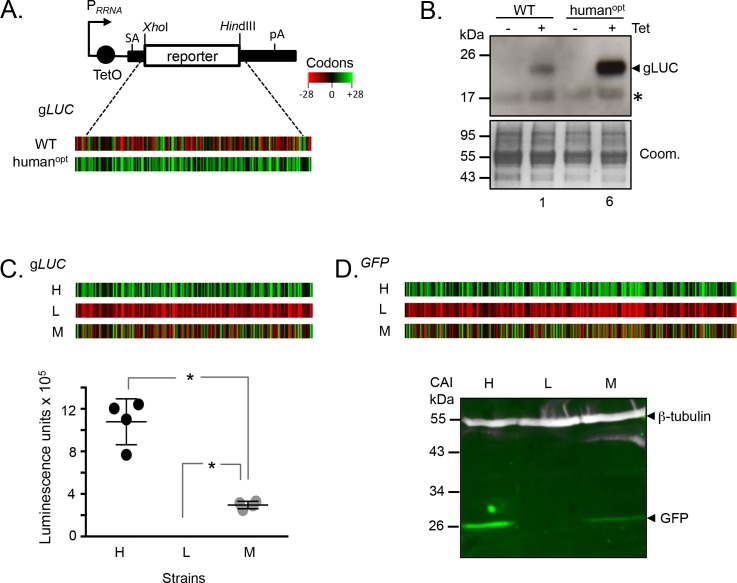
Figure 1. Protein expression is increased by GC3 codons in T.brucei.
(A) Schematic map of the pRPai-based, tetracycline-inducible reporter construct. Relevant restriction sites are shown. Black bars, tubulin untranslated regions; arrow, pol-I promoter; pA, polyadenylation site; SA, splice-acceptor site. The heat-maps of the wild-type and human codon optimised gLUC genes indicate level (percentage) of codon over-representation (green) and under-representation (red) in highly expressed genes. (B) Protein blot analysis of gLUC expression in T. brucei. *, cross-reactive band. The Coomassie-stained panel serves as a loading control; the strong band at approximately 55 kDa is the abundant Variant Surface Glycoprotein (VSG). The numbers indicate proportional luciferase expression, based on densitometry. Three independent clones gave similar results for each construct. (C) The heat-maps of synthetic gLUC reporter genes indicate codon usage as in A above. The plot indicates luciferase activity for each reporter in T. brucei; four readings from two independent strains. Error bars, standard deviation. *, p<0.0001; one-way ANOVA test. (D) The heat-maps of synthetic GFP reporter genes indicate codon usage as in A above. The LICOR protein blot indicates GFP expression for each reporter in T. brucei; β-tubulin serves as a loading control. Two independent clones gave similar results for each construct.