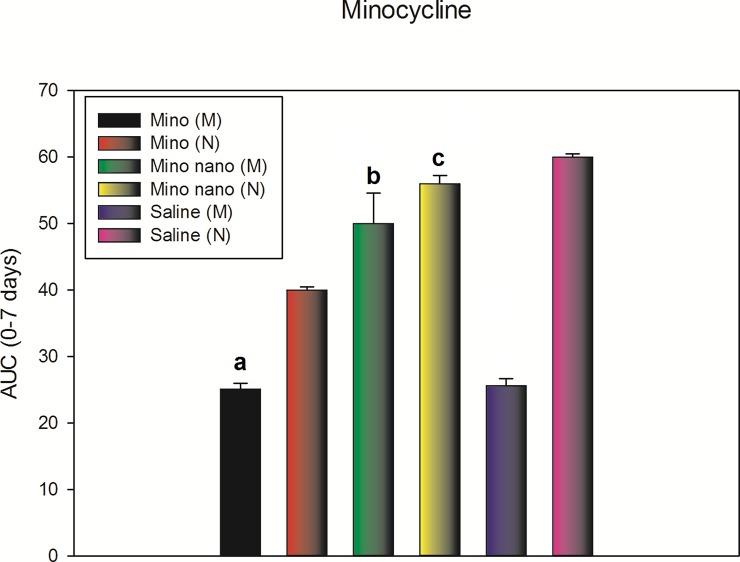
Fig 6. The figure shows the AUC of the intrathecal injections of free minocycline in monoarthritic rats (Mino (M)); intrathecal injections of free minocycline in normal rats (Mino (N)); minocycline encapsulated into SLN in monoarthritic rats (Mino nano (M)); minocycline encapsulated into SLN in normal rats (Mino nano (N)); Monoarthritic rat injected only with artificial CSF (Saline (M)), and normal rats injected only with artificial cerebrospinal fluid (Saline (N)), expressed as the AUC taken from time zero to seven days.
(Specifically, day 15 after the induction of monoarthritis, then at day 16 a Randall-Selitto test, followed by day 17, 19 and 21). There were significant differences when comparing “a” with “b" or "c", but not between “b” and “c”, meaning there was a similar antinociceptive effect of the Mino nano (M) rats compared to Mino nano (N) despite the fact the dose was half (10 μg/rat) for Mino nano (M), compared with 20 μg/rat for Mino nano (N). Results are expressed as mean ± SE of the mean. P <0.01 (two-way ANOVA).