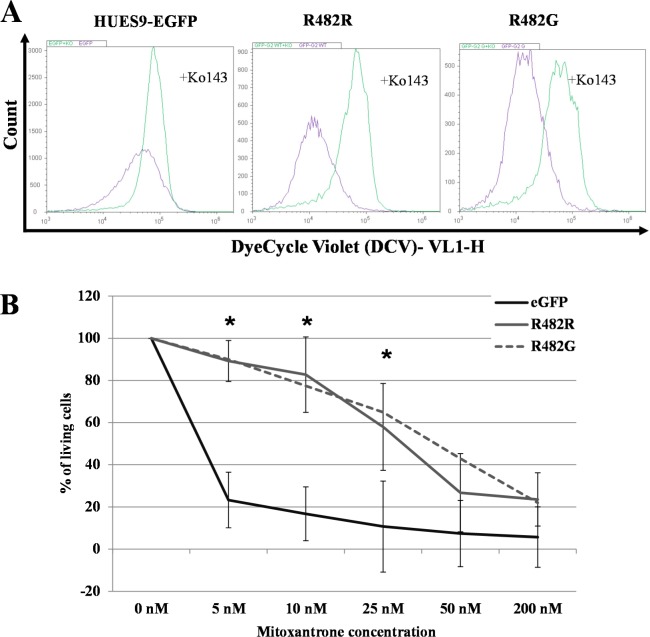
Fig 4.
Functional analysis of ABCG2 in EGFP-HUES9 (control) and GFP-ABCG2 expressing cells (A) Examination of the transport function of the GFP-ABCG2 protein variants in HUES9 cells by measuring DCV uptake. Cellular DCV fluorescence was measured in cells expressing the R482R (wild-type) and R482G (substrate mutant) variants of GFP-ABCG2. The purple histogram shows the signal of the DCV in the control cells and the green histogram shows the signal of DCV in the Ko143-treated cells. (B) Analysis of mitoxantrone cytotoxicity in EGFP-HUES9 (control) cells and in HUES9 cells expressing GFP-ABCG2 variants. Survival of parental and GFP-ABCG2 expressing HUES9 cells was measured in the presence of 5–200 nM Mitoxantrone (MX) by flow- cytometry. The ratio of the dead and living cells was calculated on the basis of propidium-iodide accumulation and was normalized to untreated cells. Values represent the means±S.D. of 3 independent experiments. Significant differences (Student’s t-test, P<0.01) in the survival of parental and ABCG2-variants expressing clones are indicated by asterisks. The exact mean±S.D. and p values are presented in S1 Table.