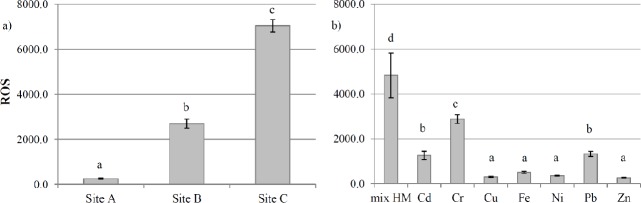
Fig 4.
ROS content in L. riparium exposed in bags at sites A, B and C of Sarno River (in-field experiment, left panel, a) and in vitro cultured with mixtures of toxic metal or with the single toxic metal at the concentrations measured in site C (CdCl2 0.14 mg l-1, Cr(Cl) 3 9.05 mg l-1, CuSO4 2.45 mg l-1, FeCl2 308.0 mg l-1, NiCl2 3.4 mg l-1, Pb(CH3COO)2 0.85 mg l-1, ZnCl2 46.76 mg l-1) (right panel, b). Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). The ROS quantity was monitored by fluorescence (excitation wavelength of 350 nm and emission wavelength of 600 nm). Bars not accompanied by the same letter are significantly different at p < 0.05, using post hoc Student-Neuman-Keuls test.