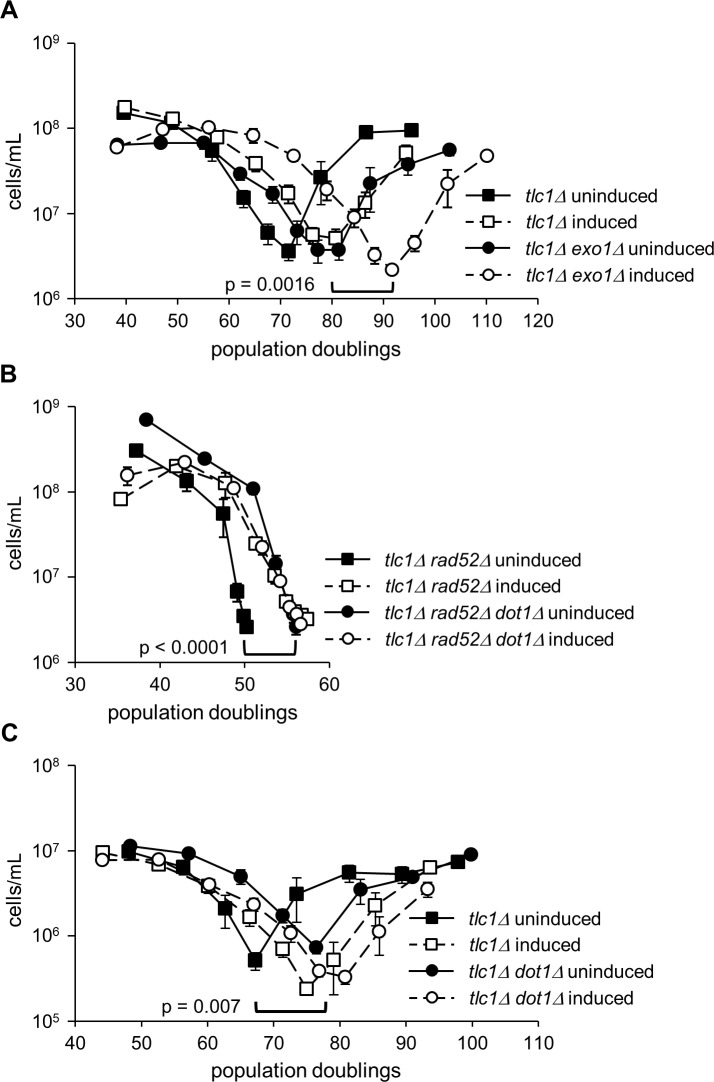
Fig 3. The anti-TERRA senescence delay is independent of Exo1 and Rad52 but is dependent on Dot1.
(A) Anti-TERRA delays senescence in tlc1Δ exo1Δ mutants. TLC1/tlc1Δ EXO1/exo1Δ were sporulated and senescence assays of tlc1Δ and tlc1Δ exo1Δ (n = 5 each) were performed with anti-TERRA either induced or uninduced. Anti-TERRA and exo1Δ each significantly delay senescence (tlc1Δ uninduced versus tlc1Δ induced, 10 PD, p < 0.002 and tlc1Δ uninduced versus tlc1Δ exo1Δ uninduced, 9 PD, p = 0.001). Together they delay senescence even further (tlc1Δ exo1Δ uninduced versus tlc1Δ exo1Δ induced, 13 PD, p = 0.0016). (B) Anti-TERRA delays senescence in tlc1Δ rad52Δ mutants but not tlc1Δ rad52Δ dot1Δ mutants. TLC1/tlc1Δ RAD52/rad52Δ DOT1/dot1Δ diploids were sporulated and senescence assays of tlc1Δ rad52Δ (n = 5) and tlc1Δ rad52Δ dot1Δ (n = 6) were performed with anti-TERRA either induced or uninduced. Both anti-TERRA and dot1Δ delay senescence in the absence of Rad52 (tlc1Δ rad52Δ uninduced versus tlc1Δ rad52Δ induced, 10 PD, p < 0.0001 and tlc1Δ rad52Δ uninduced versus tlc1Δ rad52Δ dot1Δ uninduced, 9 PD, p = 0.005), but anti-TERRA does not cause a further delay in the absence of Dot1 (tlc1Δ rad52Δ dot1Δ uninduced versus tlc1Δ rad52Δ dot1Δ induced, p = 0.563). (C) Same as in (A) except that dot1 deletion was tested instead of exo1 deletion. Anti-TERRA and dot1Δ each delay senescence (tlc1Δ uninduced versus tlc1Δ induced, 8 PD, p = 0.002 and tlc1Δ uninduced versus tlc1Δ dot1Δ uninduced, 9 PD, p = 0.007). But again, anti-TERRA does not cause a further delay in the absence of Dot1 (tlc1Δ dot1Δ uninduced vs. tlc1Δ dot1Δ induced 1.5 PD, p = 0.238). In all panels, each data point represents the mean PD versus the mean and SEM of the cell density.