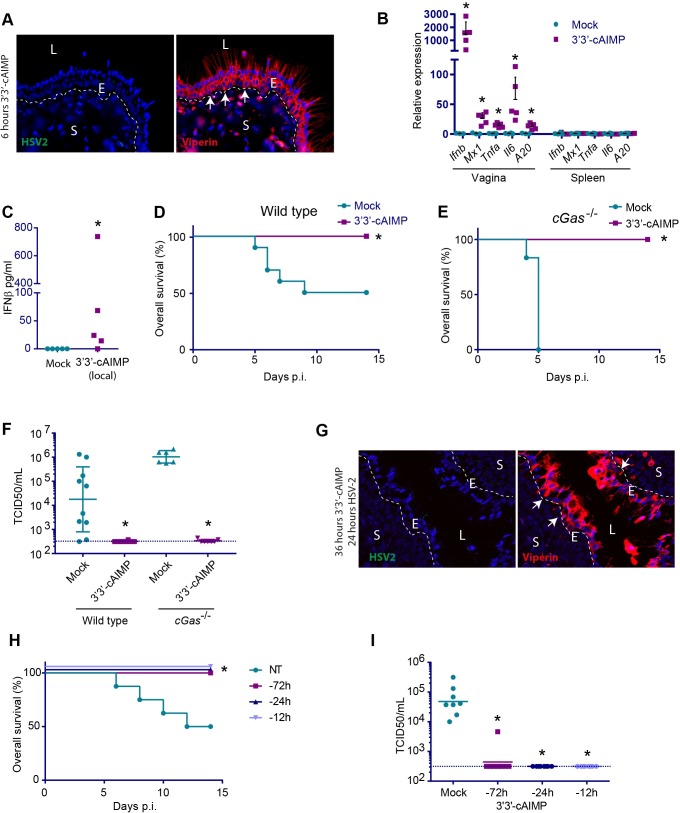
Fig 5. Local application of STING agonists protects against genital HSV2 infection.
Mice were anesthetized for 30 min and 250 μg 3’3’-cAIMP was applied to the vagina. (A) Tissues were isolated from mice 6 h after CDN stimulation. Paraffin sections of the vaginal tissues were stained for viperin (red) and HSV2 (green). DAPI (blue) marks the nuclei and the dotted white lines mark basal membrane between the epithelium and stroma. White arrows highlight examples of viperin positive cells. L = lumen, E = epithelium, S = stroma. n = 4. One representative picture is shown for each staining. (B) After 6 hours of 3’3’-cAIMP treatment (no infection), gene expression was measured in vaginal and spleen samples. The expression levels were normalized to GAPDH. n = 3–5. * = p<0.05. (C) IFNβ levels. in serum from mice treated with 3’3’-cAIMP for 6 hours. n = 5. (D, E) Overall survival for wildtype (D) or cGas-/- (E) mice treated with 3’3’-cAIMP and infected with HSV2 12 h later. n = 6–10. * = p<0,05 compared to mock. (F) HSV2 titer (TCID50) in vaginal washes (48 hours p.i.) from wildtype or cGas-/-mice treated with 3’3’-cAIMP and infected with HSV2 12 h later. n = 6–10. * = p<0,05 compared to mock treated in the same genotype. (G) Tissues were isolated from mice treated intravaginally for 12 h with 3’3’-cAIMP followed by 24 h infection with HSV-2. The samples were prepared and analyzed as in A. (H) Overall survival and (I) virus load for wildtype mice pre-treated with 3’3’-cAIMP 12, 24 or 72 h prior to virus infection. n = 8. * = p<0,05 compared to mock treated group. Statistics, (B) Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. (C, F, I) Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon U test. (D, E, H) Log-rank test.