Figure 7. Gene groups differentially regulated following optic-nerve injury.
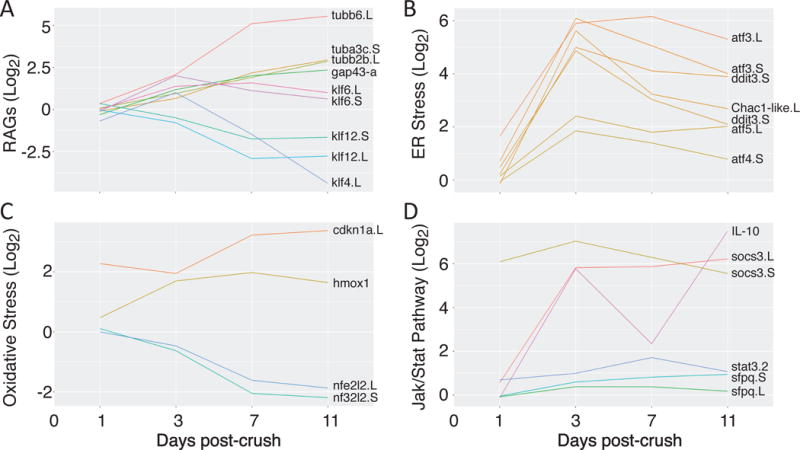
(A) Many axonal regeneration-associated genes (RAGs) and development associated factors are up-regulated following crush (tubulin, gap43, klf6), while some factors shown to inhibit axonal growth are down-regulated (klf4). (B & C) Stress response pathways shown to be up-regulated by optic nerve injury in other vertebrate species are up-regulated in Xenopus laevis RGCs as well. (D) Some members of the Jak/Stat signaling pathway are dramatically up-regulated. (A – D) In all panels, we compare the log2 ratio of expression levels for genes in the crush versus control samples. Genes with names not appended “.L” or “.S” (hmox1, IL-10), represent symbols not yet assigned in the Xenopus laevis 9.1 genome assembly. In these cases, data are shown from read alignments to a transcript reference (detailed in Materials and Methods).
