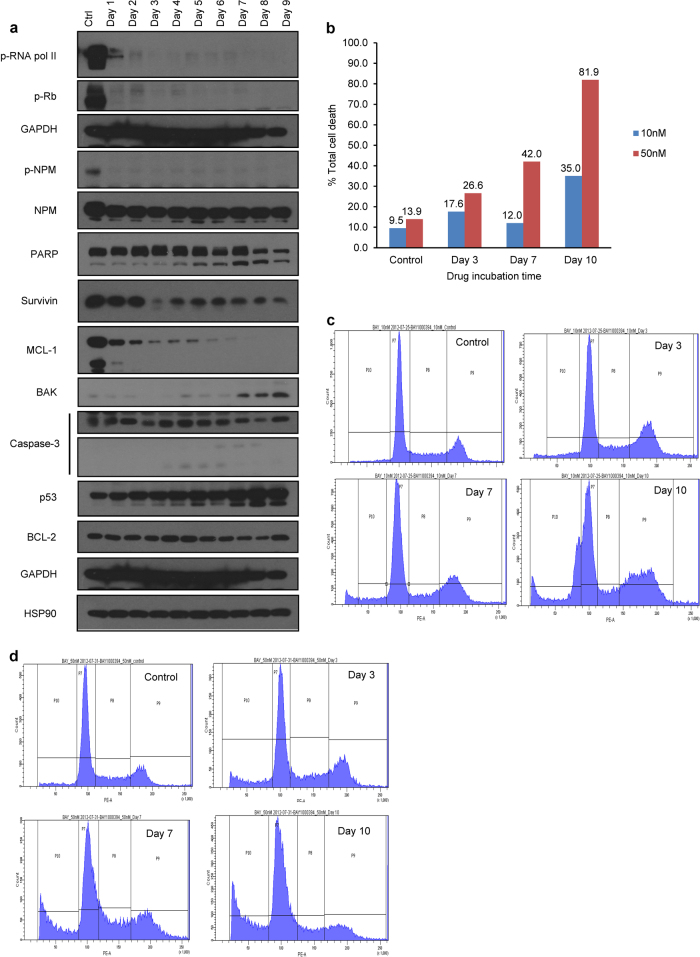
Fig. 2. Effects of roniciclib on EBV+ C666-1 cells.
a Time course and dose-dependent inhibition of direct protein substrates of CDKs in C666-1 cells. Roniciclib significantly inhibited phosphorylation of RNA-polymerase II, retinoblastoma, and nucleophosmin. Drug treatment also induced PARP activation, accompanied by a moderate decrease in survivin expression. The expression of proapoptotic proteins such as BAK, which is known to activate caspases, was enhanced along with concomitant increases in activated caspase-3 and p53 and a decrease in the anti-apoptotic protein MCL-1. b Changes in the percentage of dead C666-1 cells over the course of drug incubation. c Apoptosis and FCM analysis of C666-1 cells treated at 10 nM. d Apoptosis and FCM analysis of C666-1 cells treated at 50 nM. c and d indicate cell death and cell cycle arrest via G2/M accumulation and subsequent shifts to G0 by days 3, 7, and 10. P7: G1 phase; P8: S phase; P9: G2/M phase; P10: G0 phase. FCM flow cytometry, EBV Epstein–Barr virus