Fig. 1.
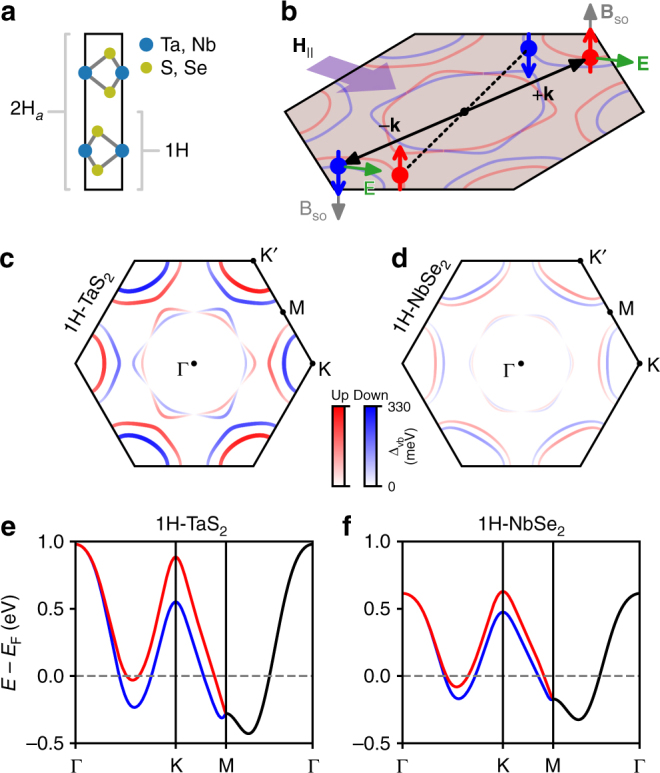
Electronic structure of monolayer metallic transition-metal dichalcogenides. a Crystal structure of 2Ha-MX2 (with transition metal atoms directly above one another along the c-axis), viewed along [100] direction for M ∈ {Nb, Ta} and X ∈ {S, Se} with 1H (monolayer) substructure indicated. b Electrons in the K and K′ valleys with spins pinned to the out-of-plane direction due to effective field Bso ∝ E × k resulting from planar crystal field and momentum. Straight black lines connect time-reverse pairs. c Spin-projected Fermi surface of monolayer TaS2 and d NbSe2 computed by density functional theory (DFT). Red corresponds to one Sz projection and blue to the opposite (e.g., up and down, respectively). Variation in the shading and curve thickness indicates the magnitude of spin-splitting in the valence band Δvb(k) due to spin–orbit coupling, with the color scale being shared between c and d to emphasize the difference in magnitudes. e Relevant bands around the Fermi level for monolayer TaS2 and f NbSe2 from DFT, with spin polarization corresponding to colors in c, black bands being spin degenerate
