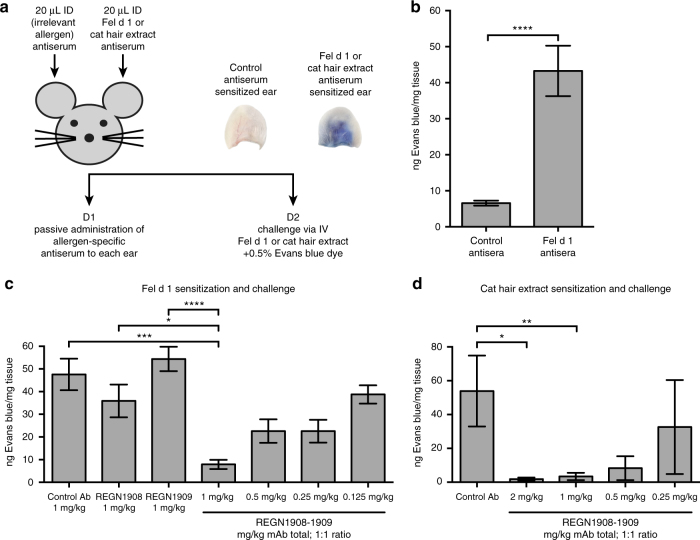
Fig. 3.
A combination of REGN1908–1909 inhibits Fel d 1-induced mast cell degranulation in vivo in the passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA) mouse model. a Schematic of the PCA mouse model. b Each mouse (n = 5 in two independent experiments) were sensitized using Fel d 1 antisera and control peanut antisera in the left and right ears, respectively, followed by challenge with 1 μg nFel d 1 one day later. Data from the pooled experiments are expressed as ng of Evans blue extracted per mg of ear tissue from ears sensitized with control antisera or ears sensitized with peanut antisera. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed paired t-test. c Balb/c mice were administered subcutaneous (SC) doses of REGN1908 (n = 15), REGN1909 (n = 15), a combination of REGN1908–1909 (1:1 ratio) at 0.125 mg/kg (n = 15), 0.25 mg/kg (n = 15), 0.5 mg/kg (n = 15), or 1 mg/kg (n = 14), or an IgG4P control antibody (n = 14) 3 days prior to initiating the PCA model using Fel d 1-specific antisera (normalized to 25ng IgE per ear) and 1 µg Fel d 1 challenge. The number per group represents pooled data from three independent experiments. d Balb/c mice were administered SC injections of a combination of REGN1908–1909 (1:1 ratio) at 0.25 mg/kg (n = 5), 0.5 mg/kg (n = 5), or 1 mg/kg (n = 5), or 2 mg/kg (n = 5), or an IgG4P control antibody (n = 5) 3 days prior to initiating the PCA model using cat extract antisera normalized to 25ng IgE per ear and 250 BAU cat hair extract challenge. Results of one experiment are shown. c, d Data are expressed as ng of Evans blue extracted per mg of ear tissue based on the value obtained from each control peanut ear subtracted from the corresponding value from the challenge ear. Statistical significance was determined using the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by the Dunn’s post hoc test (c–d). Data are presented as mean ± SE. **** p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05