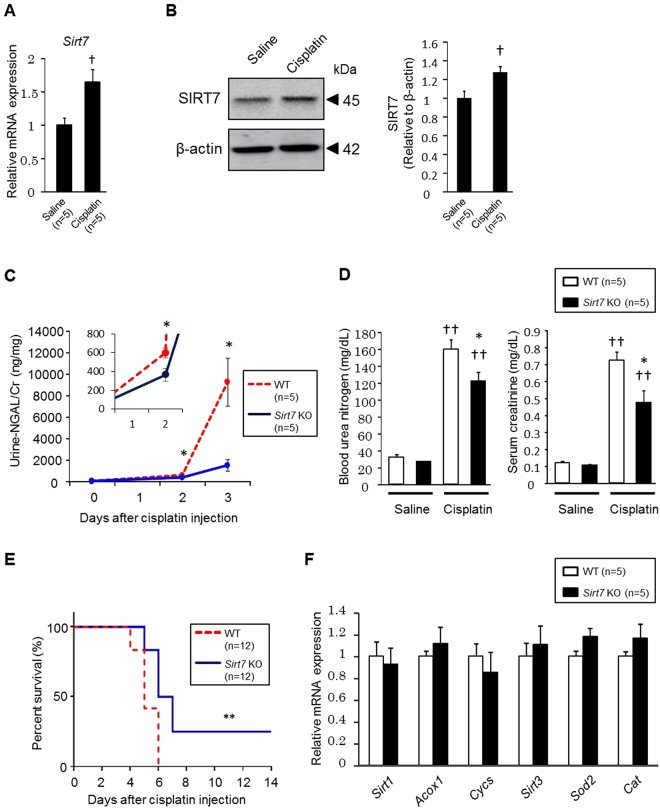
Figure 2.
Deletion of SIRT7 ameliorates cisplatin-induced kidney injury. (A) Sirt7 mRNA expression in the kidney of WT mice was determined by real-time PCR (n = 5/group). (B) SIRT7 protein expression in the kidney of WT mice was evaluated. β-actin was used as a loading control (n = 5/group). (C) Urine was collected for 24 h using metabolic cages, and urinary NGAL/creatinine levels were determined at each time point (n = 5/group). (D) Blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine levels were measured at day 3 in the normal saline administration groups and cisplatin administration groups (n = 5/group). (E) Survival rate after cisplatin administration was assessed until day 14 (n = 12/group). (F) mRNA expression of Sirt1, Sirt3, and their target genes in the cisplatin-treated kidney of WT and Sirt7 KO mice was determined by real-time PCR (n = 5/group). *WT vs. Sirt7 KO, p < 0.05; **WT vs. Sirt7 KO, p < 0.01; †saline vs. cisplatin, p < 0.05; ††saline vs. cisplatin, p < 0.01. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM.