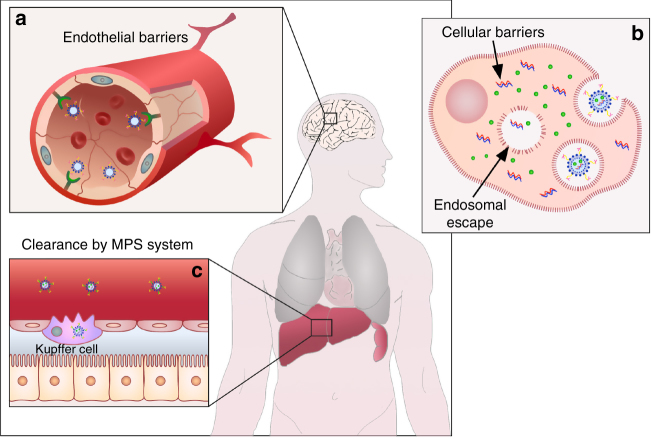
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of main physiological barriers faced by passive and active targeted NCs. a NCs face endothelial barriers in the process of their extravasation into the tumor tissue; illustration of the blood–brain barrier as an example. b Uptake of NCs by the target cells and their escape from the endo-lysosomal system into the cytotosl are the major cellular barriers. c Hepatic Kupffer cells as an example of mononuclear phagocytic system (MPS), which results in the clearence of systemically administered NCs, reducing their half-life and effective dose