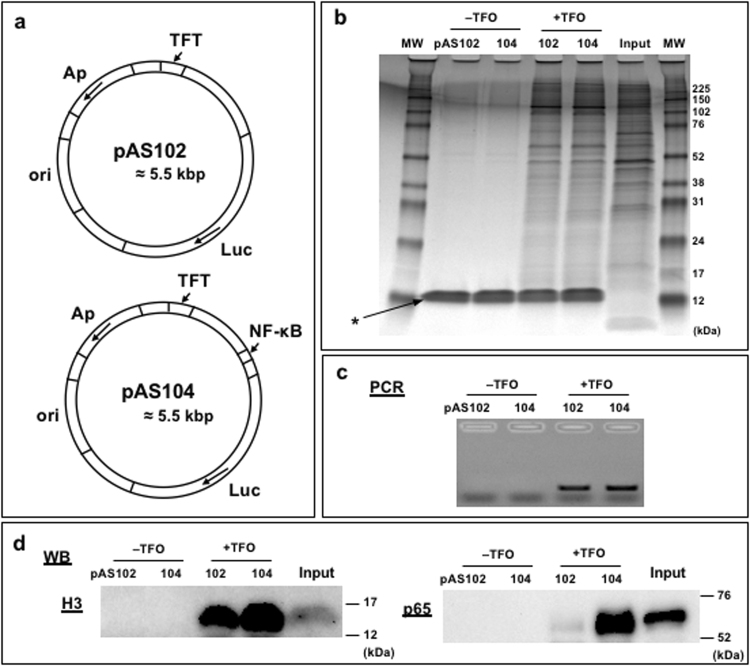
Figure 4.
Isolation of NF-κB proteins from human nuclear extracts via IDAP: (a) Schematic structure of the plasmids. A model NF-κB binding site is only present in plasmid pAS104, not in pAS102. ori: high copy number pUC origin in E. coli. Luc: Luciferase gene for a reporter assay. Ap: ampicillin resistance gene. TFT: Triplex Forming Tag. NF-κB: a binding site for NF-κB proteins. (b) Protein detection via silver staining. 80 ng of plasmids are incubated with ≈ 2.4 × 106 cells equivalent of human nuclear extracts. 20% of the elution products are loaded. Lanes are pAS102 or pAS104 in absence or presence of TFO. Input (nuclear extracts) from ≈ 2.5 × 104 cells is loaded. MW: molecular weight marker. *: streptavidin (c) Plasmid detection via PCR. PCR quantification was performed as detailed in Fig. 6d. 0.003% of the elution products are used as a template. (d) Protein detection via WB. For histone H3 detection: 50% of the elution products and Input (nuclear extracts) from ≈ 1 × 105 cells are loaded; For p65 detection: 22% of the elution products and Input (nuclear extracts) from ≈ 2.5 × 104 cells are loaded. The set of experiments (b ~ d) were independently performed four times with similar results. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S8.