Fig. 1.
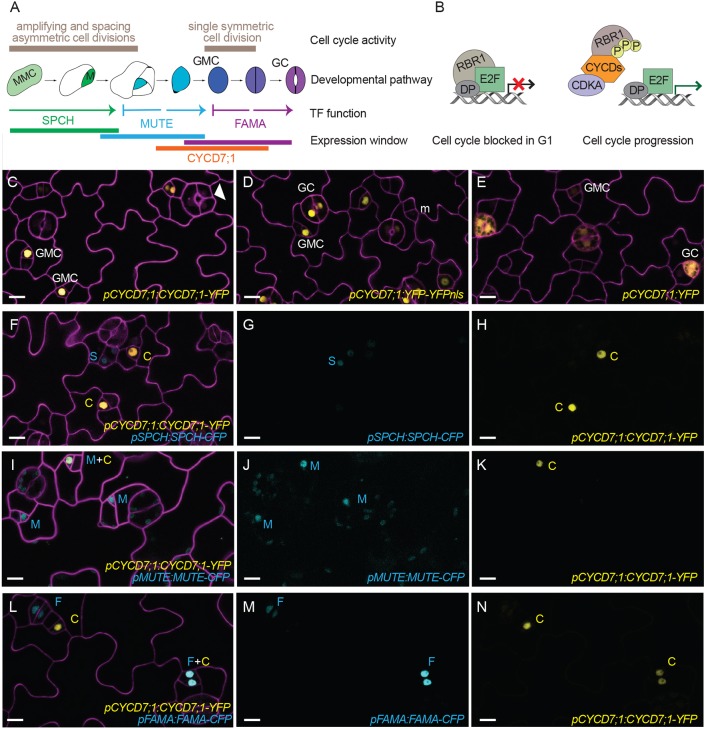
CYCD7;1 is expressed in GMCs prior to the last symmetric division of the stomatal lineage. (A) Schematic of stomatal development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell cycle activity, depicted in beige, along with cell fate transitions, transcription factor (TF) function and expression window of the master bHLH transcription factors SPCH (green), MUTE (blue), and FAMA (purple) and CYCD7;1 (orange) are shown. Meristemoid mother cells (MMC, light green) divide asymmetrically to enter the lineage. Meristemoids (green) can undergo amplifying and spacing asymmetric cell divisions until activity is terminated. Guard mother cells (GMC, blue) reenter the cell cycle only once to generate the pair of symmetric guard cells (GC, purple). (B) Plant RBR1/CYCD complexes driving the G1 to S transition and commitment to divide. RBR1 binds to E2F-DP transcription factors and blocks their ability to induce transcription of S phase genes. CYCDs interact with RBR1 through their LxCxE motif and facilitate phosphorylation of RBR1 by the CDKA;1/CYCD complex. Upon phosphorylation, RBR1 releases E2F transcription factors, which leads to expression of S phase genes for DNA replication. (C-E) Expression of the translational reporter pCYCD7;1:CYCD7;1-YFP, and the transcriptional reporters pCYCD7;1:YFP-YFPnls and pCYCD7;1:YFP (all yellow), in abaxial cotyledons. White arrowhead points at ectopic cell divisions. (F-N) Co-expression of pCYCD7;1:CYCD7;1-YFP (yellow, C) and pSPCH:SPCH-CFP (cyan, S), pMUTE:MUTE-CFP (cyan, M) and pFAMA:FAMA-CFP (cyan, F). Confocal images were taken at 5 dag. Cell outlines (magenta) are visualized with propidium iodide. All images are at the same magnification. Scale bars: 10 μm.