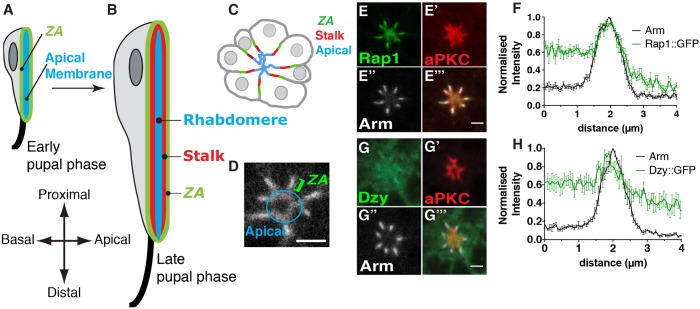
Fig. 1.
Dizzy and Rap1 are ZA-associated proteins. (A,B) Schematic representation of the developing pupal photoreceptor. (A) Early and (B) late stage pupal photoreceptors shown along the lens (top) to brain (bottom) axis of the retina. The apical membrane, which is clearly differentiated by mid pupation and by late pupation forms the rhabdomere, is depicted in blue. The stalk membranes are depicted in red and the ZA in green. The axon is depicted as a black line, at the bottom (brain or distal pole) of the cell. (C) Cross section of a cluster (ommatidium) of photoreceptors at mid pupation when the ZA (green), stalk membrane (red) and apical membrane (blue) have been specified. (D) Annotated magnification of the Rap1::GFP staining showing the apical membrane and the ZA. (E–E‴) Photoreceptors expressing Rap1::GFP (E), stained for aPKC (E′) and Arm (E″). Scale bar: 2 µm. (F) Intensity profiles of Rap1::GFP and Arm measured along the apical-basal axis. Results are mean±s.e.m. (n=8 cells from 3 retinas). (G–G‴) Photoreceptors expressing Dzy::GFP (G), stained for aPKC (G′) and Arm (G″). Scale bar: 1.5 µm. (H) Intensity profiles of Dzy::GFP and Arm measured along the apical-basal axis. Results are mean±s.e.m. (n=6 cells from 3 retinas).