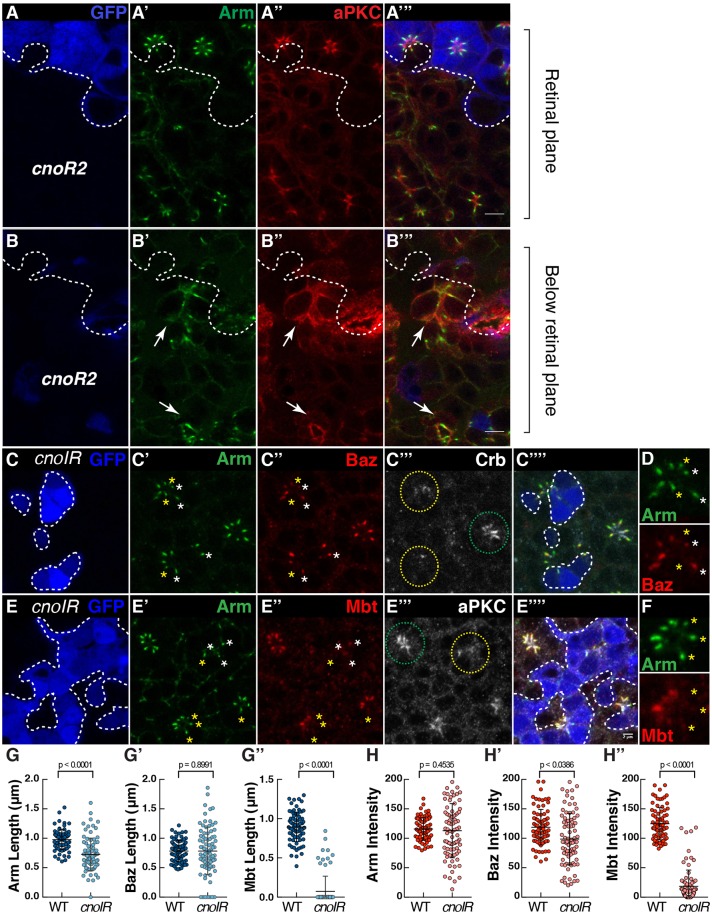
Fig. 4.
Cno regulates the coupling of Arm, Baz and Mbt at the developing ZA. (A–B) cnoR2 mutant cells (lacking GFP, blue, the contour of which is denoted by the dashed line, A,B) stained for Arm (A′,B′) and aPKC (A″,B″). White arrows indicate cnoR2 mutant photoreceptors that have delaminated from the retinal neuroepithelium. (C–F) cnoIR clones positively labeled by GFP (blue, C,E) and stained for Arm (C′,E′), Baz (C″), Crb (C‴), Mbt (E″) and aPKC (E‴). Green and yellow circles outline wild-type and cnoIR ommatidia, respectively. (D,F) A magnification of one mosaic ommatidium to highlight the absence of Baz (D) or Mbt (F) in some of the Arm domains. White stars label ZAs containing both Arm and Baz, while yellow stars indicate ZAs containing Arm but depleted for Baz (D) or containing Arm but depleted for Mbt (F). Scale bars: 2 μm. (G–G″) Quantification of Arm (G), Baz (G′) and Mbt (G″) domain length at the ZA. (H–H″) Quantification of Arm (H), Baz (H′) and Mbt (H″) mean pixel intensity at the ZA. All error bars are s.d. (n≥77 from 5 retinas).