Fig. 5.
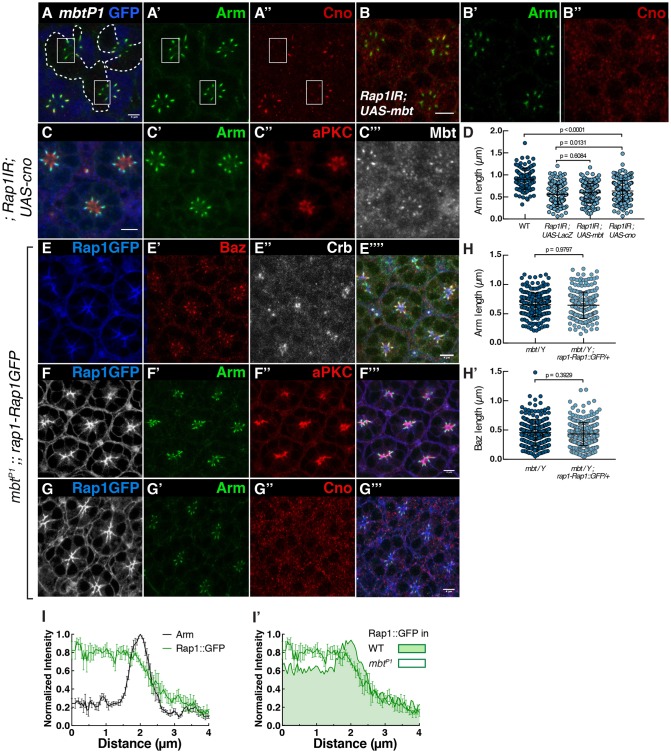
Mbt is required for the accumulation of Cno and enrichment of Rap1 at the ZA. (A) mbtP1 mutant photoreceptors (lacking GFP, blue, the contour of which is denoted by the dashed line, A) and stained for Arm (A′) and Cno (A″). White boxes highlight ZAs within the mbtP1 mutant tissue. (B) Rap1IR photoreceptors expressing Mbt and stained for Arm (B′) and Cno (B″). (C) Rap1IR photoreceptors expressing Cno and labeled for Arm (C′), aPKC (C″) and Mbt (C‴). (D) Quantification of the Arm domain length at the ZA in wild-type photoreceptors, and for Rap1IR photoreceptors co-expressing UAS-LacZ, UAS-mbt or UAS-cno driven by NP-Gal42631. Results are mean±s.d. (n≥105 from 4 retinas). (E–G) mbtP1 mutant photoreceptors expressing rap1-Rap1::GFP (E,F,G) stained for Baz (E′), Arm (F′,G′), Crb (E″), aPKC (F″) and Cno (G″). (H) Quantification of the length of the Arm (H) and Baz (H′) domains at the ZA in the mbtP1 mutant and mbtP1 mutants expressing rap1-Rap1::GFP. Results are mean±s.d. (n≥187 from 4 retinas). (I) Intensity profiles measured for Rap1::GFP and Arm along the apical-basal axis in mbtP1 photoreceptors. (I′) Comparison of intensity profiles of Rap1::GFP measured in mbtP1 photoreceptors compared to that of wild-type photoreceptors (shaded). Results are mean±s.e.m. (n≥6 cells from 3 retinas). Scale bars: 2 μm.