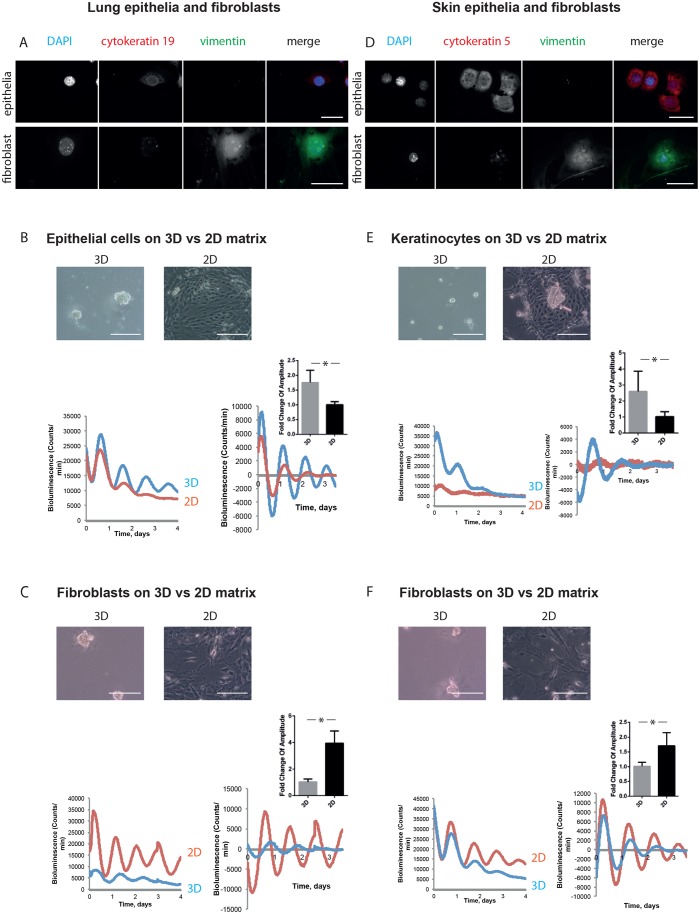
Fig. 2.
Epithelia and fibroblasts from other tissues have inverse responses to mechanical stimuli. (A) Immunofluorescence staining revealed lung epithelial cells as a population that is cytokeratin-positive and vimentin-negative. In contrast, lung fibroblasts are cytokeratin negative and vimentin positive. DAPI, blue; cytokeratin 19, red; vimentin, green (single-channel images shown in grey scale). Scale bar: 50 µm. (B) Lung epithelial cells have stronger circadian rhythms in 3D culture than 2D. Phase-contrast images above. Bioluminescence traces below, presented as raw (left) and normalised (right), with fold-change graph above. (Student's t-test, P<0.05, mean±s.e.m.). (C) Lung fibroblasts have weaker circadian rhythms in 3D culture than 2D. Phase-contrast images above. Bioluminescence traces below, presented as raw (left) and normalised (right), with fold-change graph above. (Student's t-test, P<0.05, mean±s.e.m.). (D) Keratinocyte isolation produces a population that is cytokeratin-positive and vimentin-negative. Dermal fibroblasts are a population that is cytokeratin-negative and vimentin-positive. DAPI, blue; cytokeratin 5, red; vimentin, green. Scale bar: 50 µm. (E) Keratinocytes have stronger circadian rhythms in 3D culture than 2D. Phase-contrast images above. Bioluminescence traces below, presented as raw (left) and normalised (right), with fold-change graph above. (Student's t-test, P<0.05, mean±s.e.m.). (F) Dermal fibroblasts have weaker circadian rhythms in 3D culture than 2D. Phase-contrast images above. Bioluminescence traces below, presented as raw (left) and normalised (right), with fold-change graph above. (Student's t-test, P<0.05, mean±s.e.m.). For lung epithelia, 3 independent biological replicates were performed, each with 3 animals, which were pooled together to form 2 cultures per condition. For lung fibroblasts, 3 independent biological replicates were performed, each with 2 animals, which were pooled together to form 2 cultures per condition. For keratinocytes, 3 independent biological replicates were performed, each with 5 animals, which were pooled together to form 2 cultures per condition. For dermal fibroblasts, 3 independent biological replicates were performed, each with 5 animals, which were pooled together to form 2 cultures per condition.