FIGURE 2.
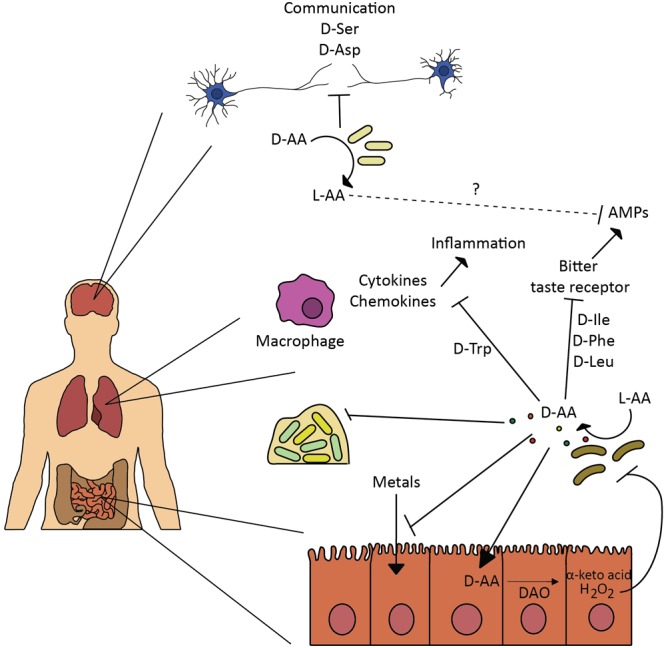
Effect of D-amino acids on human host. Bacteria are involved in various physiological processes in the human body by regulating L- and D-amino acid availability. Such modulation affects neural communication (Kawase et al., 2017), inflammation response induced by cytokines and chemokines (Kepert et al., 2017), production of anti-microbial peptides (AMPs) through inhibition of bitter taste receptors-signaling mechanism (Lee et al., 2017), and metals absorption (Ghssein et al., 2016). Bacteria secrete D-amino acids to inhibit growth and biofilm of competitors (Rasmussen et al., 2000; Lee et al., 2017), in similar fashion bacterial released D-amino acids and interplay with the intestinal D-amino acid oxidase modulate gut homeostasis and microbiota composition (Sasabe et al., 2016).
