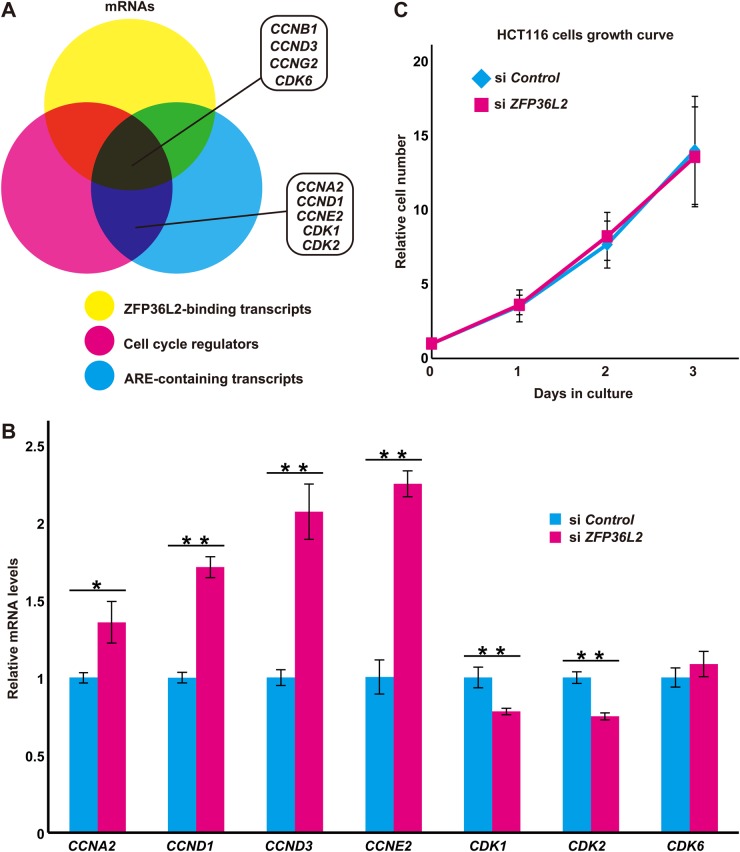
Fig. 5.
ZFP36L2 suppresses the G1/S cyclin expressions. (A) Venn diagram of cell cycle-related transcripts (shown as magenta) showing the overlap between mRNAs that were bound to ZFP36L2 (Zhang et al., 2013; shown as yellow) and mRNAs with AREs in their 3′-UTRs (Bakheet et al., 2006; shown as cyan). (B) Results of quantitative real-time RT-PCR analyses for potential targets of ZFP36L2 in ZFP36L2 knockdown HCT116 cells. Knockdown of endogenous ZFP36L2 stimulates the expression of G1/S cyclin transcripts, including cyclin A2 (CCNA2), cyclin D1 (CCND1), cyclin D3 (CCND3), and cyclin E2 (CCNE2), while the expression of CDK genes was not affected. Efficacy of ZFP36L2 knockdown was verified by anti-Flag-ZFP36L2 immunoblot analysis (see also Fig. S3C). Data represent mean±s.d. calculated from three independent biological replicates. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 compared with control siRNA cells. (C) Knockdown of ZFP36L2 expression does not affect the normal proliferation of HCT116 cells. Growth curves of HCT116 cells transfected with ZFP36L2 siRNA or control siRNA. Efficacy of ZFP36L2 knockdown was verified by anti-Flag-ZFP36L2 immunoblot analysis (see also Fig. S3C). Data represent mean±s.d. calculated from at least three independent biological replicates.