Figure 1.
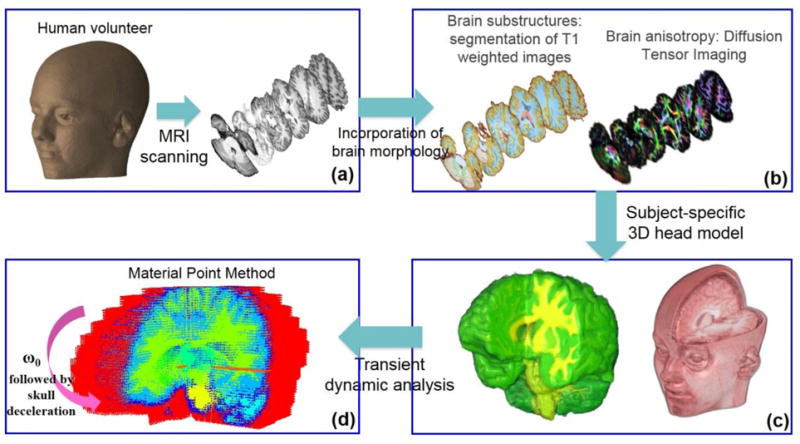
3D computational human head model. The model was constructed from the T1 and diffusion MRI images of a human volunteer. T1-weighted images were used to segment brain tissue into different substructures (a). Diffusion images provided information on fiber orientation and fractional anisotropy of the brain tissue (b). Individual images were stacked together to generate a 3D model (c). Resulting model was subjected to mild angular acceleration and solved using Material Point Method (MPM) (d).
