Figure 3. Mesh size mediates drug diffusion.
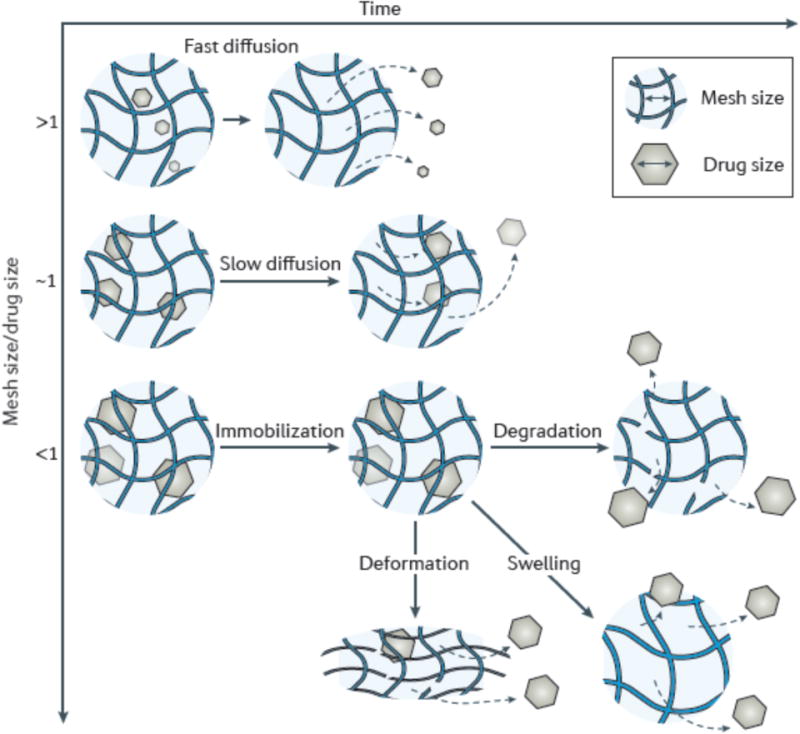
a| A small drug relative to the mesh size diffuses rapidly through the hydrogel, resulting in a short release duration. b| When the size of drug approaches the mesh size (rmesh/rdrug ≈ 1), drug release is dramatically slowed. c| When the drug is larger than the mesh size (rmesh/rdrug <1), drugs are physically entrapped inside the network. To release the originally immobilized drugs, the mesh size can be enlarged through network degradation (d), swelling (e), or via applying deformation to disrupt the network (f). The gray dashed lines refer to the diffusion pathway of drugs.
