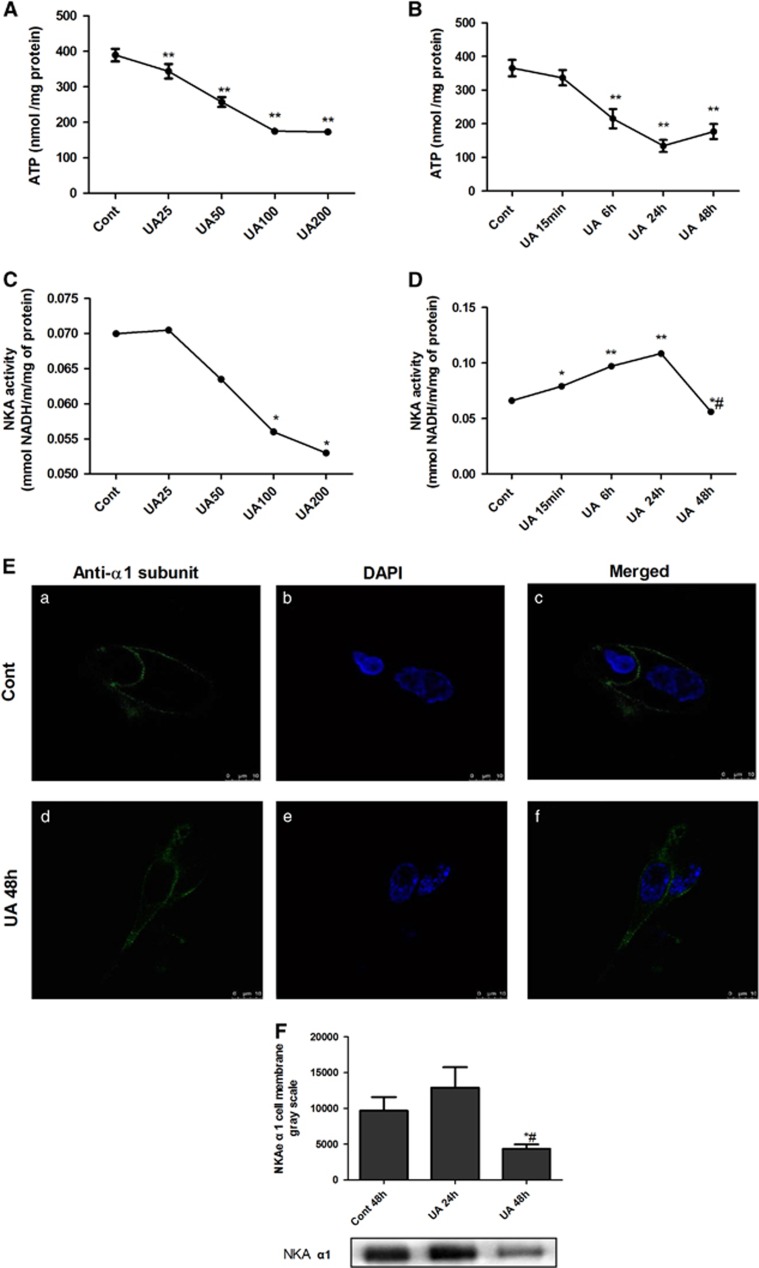
Figure 1.
UA dose- and time-dependently reduced intracellular ATP levels altered NKA activity and its α1 subunit cellular expression in human PTECs. PTECs were incubated with different concentrations of UA (25 to 200 μg ml−1) for 48 h or different time courses (15 min to 48 h of 100 μg ml−1 UA). UA dose- (A) and time-dependently (B) reduced intracellular ATP levels. UA 25 μg ml−1 exhibited a tendency to increase NKA activity, but UA concentrations of 100 μg ml−1 started to dose-dependently reduce the NKA activity (C). UA100 μg ml−1 time-dependently affected the NKA activity, with the maximal increased NKA activity at 24 h that started to decrease until 48 h (D). Immunofluorescence showed that the expression of the α1 subunit of NKA (green) was linearly expressed on the cell surface, but when the cells were incubated with 100 μg ml−1 UA for 48 h, NKA α1 membrane expression was reduced and scattered in the cytoplasm (E). Immunoblotting of cell surface proteins confirmed the changed cell membrane expression of the α1 subunit. Twenty-four hours of incubation of 100 μg ml−1 UA increased the α1 subunit, but 48 h of incubation of UA reduced the α1 subunit expression on the cell surface of PTECs (F). *P<0.05 vs Cont, **P<0.01 vs Cont, #P<0.05 vs UA 24 h.