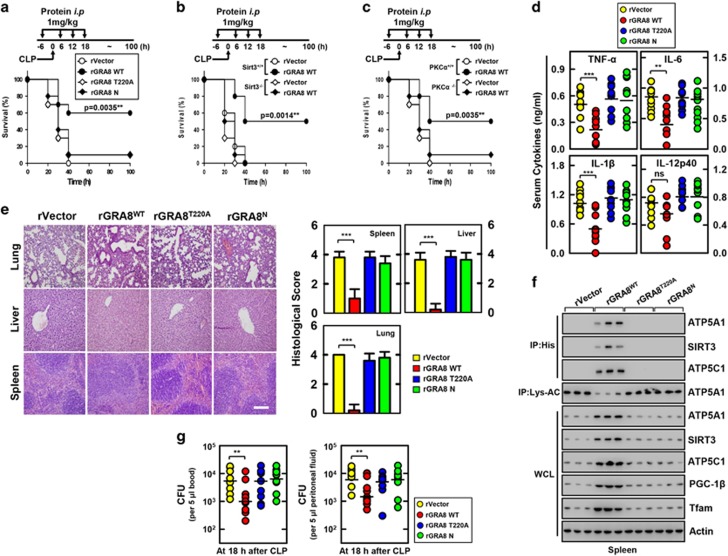
Figure 6.
The rGRA8 protects mice from cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced polymicrobial sepsis. (a–c) Schematic of the CLP model treated with rGRA8 or its mutants (upper). The survival of mice was monitored for 7 days; mortality was measured for n=25 mice per group (lower). Statistical differences compared with the rVector-treated mice are indicated (log-rank test). The data are representative of two independent experiments with similar results. (d) Serum cytokine levels and (e) representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of the lung, liver and spleen (left) from 10 mice per group. Histopathology scores were obtained from H&E stained as described in Methods (right) were determined at 30 h in CLP mice were treated with rGRA8 or its mutants. Scale bar, 200 μm. (f) Splenocytes were used for immunoprecipitation (IP) with αHis or αLys-AC, followed by immunoblotting (IB) with αATP5A1, αATP5C1 or αSIRT3. Whole cell lysates (WCLs) were used for IB with αATP5A1, αATP5C1, αSIRT3, αPGC-1, αTfam or αActin. The data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. (g) The bacterial burden was evaluated 18 h after treatment of CLP mice with rGRA8 or its mutants (n=10 mice per group). Results are expressed as means±s.d. (10 mice per group (d, g). Significant differences (**P<0.01; ***P<0.001) compared with rVector-treated mice (d, e right, and g).