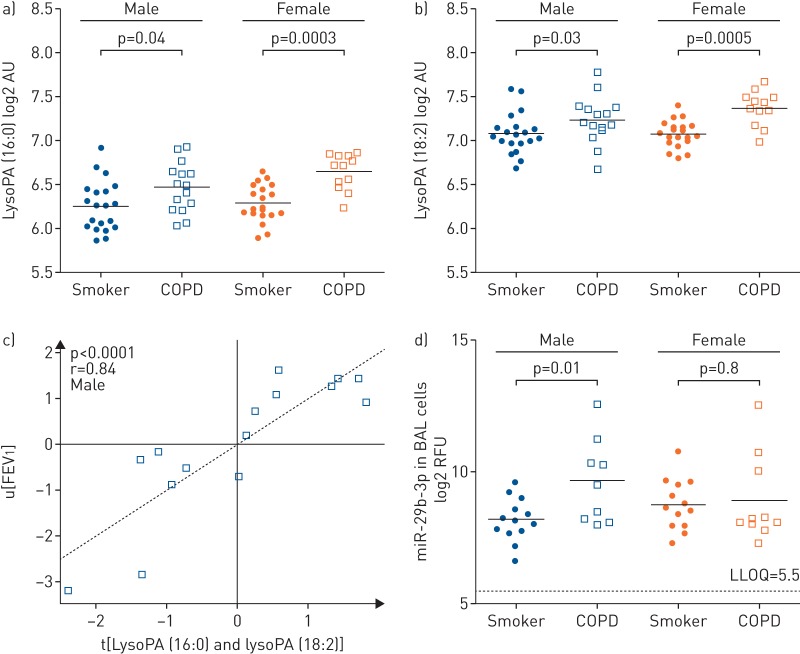
FIGURE 2.
The lyso-phosphatidic acid (lysoPA)–autotaxin axis was attenuated in males with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). a) Serum lysoPA (16:0) levels in smokers versus COPD; (b) serum lysoPA (18:2) levels in smokers versus COPD; (c) lysoPA (16:0) and lysoPA (18:2) metabolites correlated with lung function (forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1)) in male COPD patients (r=0.84, p<0.0001). No correlation was observed in the corresponding female COPD population (r=0.44, p=0.15); (d) levels of miR-29b in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells from male and female smokers and COPD patients. Values for the other members of the miR-29 family are shown in online supplementary figure E6. LysoPA data are from the nontargeted metabolomics platform and are presented as log2 of arbitrary units (AU). RFU: relative fluorescence units; LLOQ: lower limit of quantification.