Figure 1. RNASeq and co-expression gene network analyses identified TXNDC5 as a potential novel mediator of cardiac fibrosis.
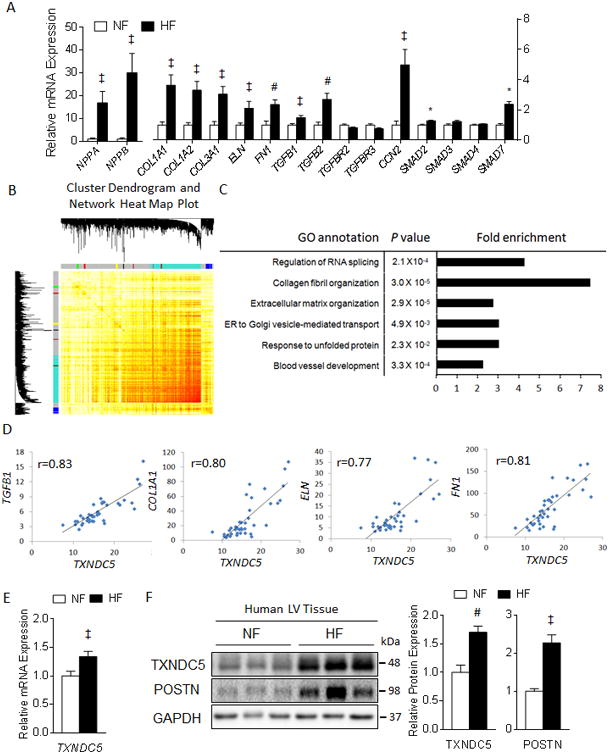
(A) RNASeq analysis revealed upregulation of fibrogenic genes (including ECM protein genes COL1A1, COL1A2, COL3A1, ELN and FN1, matricellular protein CCN2 and genes involved in TGFβ signaling such as TGFB1, TGFB2, SMAD2 and SMAD7) and HF markers (ANF/NPPA and BNP/NPPB) in human HF, compared to NF, LV. (B) Cluster dendrogram and network heat map plot of the 15 gene modules identified by Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) on the human LV RNASeq data. (C) Gene ontology analysis revealed that module Turquoise was enriched in genes that are involved in the pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis. (D) TXNDC5 expression in human LV showed strong positive correlations with TGFβ1 and ECM genes including COL1A1, ELN and FN1. The transcript (E) and protein (F) expression levels of TXNDC5 were significantly upregulated in human HF, compared to NF, LV samples (‡P<0.05, #P<0.01, *P<0.001).
