Figure 4. Knockdown of TXNDC5 in hCF led to accelerated ECM protein degradation owing to ECM protein misfolding and subsequent removal through ER-associated protein degradation (ERAD).
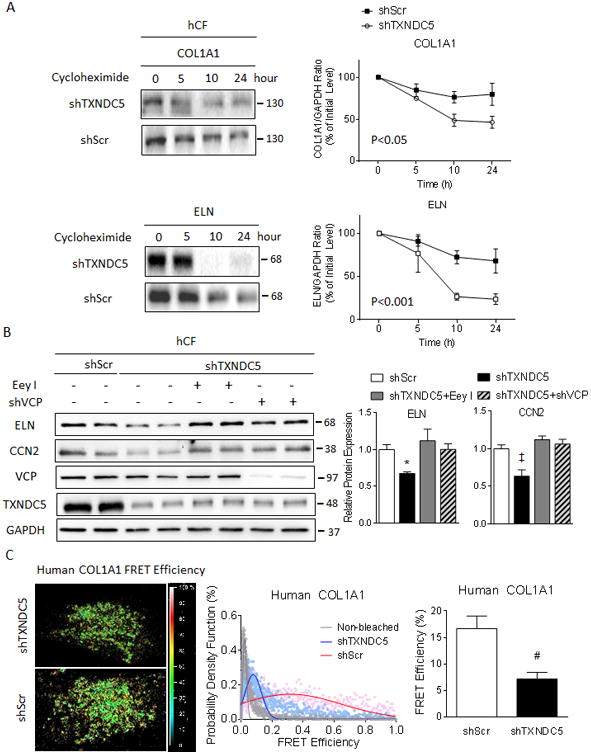
(A) A cycloheximide protein chase assay revealed accelerated degradation of COL1A1 and ELN proteins in hCF with TXNDC5 knockdown (shTXNDC5-transduced), compared to control (shScr-transduced) cells. (B) ERAD inhibitor Eey I or shVCP treatment in hCF reversed the reduction in ELN and CCN2 protein expression resulting from knockdown of TXNDC5. (C) A fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based protein folding assay using a dual fluorescence-labeled COL1A1 construct in hCF showed significantly reduced COL1A1 FRET efficiency in cells with knockdown of TXNDC5 (shTXNDC5, n=10), compared to scrambled control (shScr, n=10), indicating reduced COL1A1 folding with TXNDC5 depletion (‡P<0.05, #P<0.01, *P<0.001).
