Figure 7. TGFβ1 induces TXNDC5 expression in CF through TGFβ1-ER stress-ATF6 signaling axis.
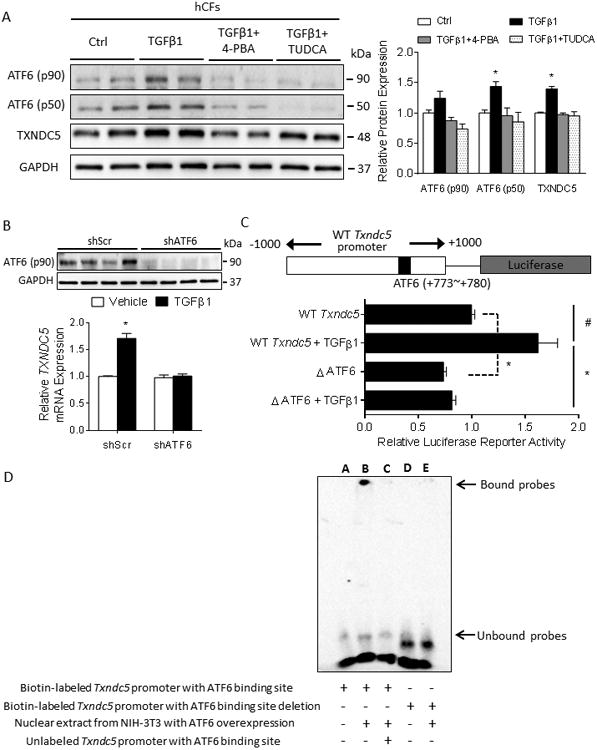
(A) TGFβ1 treatment in hCF increased ER stress (as evidenced by the upregulated ER stress markers ATF6 p50 and p90) and TXNDC5 protein expression levels, which could be abrogated by the treatment with general ER stress inhibitors 4-phenylbutyrate (4-PBA, 0.5 mmol/L) or tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA, 0.5 mmol/L) (B) Knockdown of ATF6 in hCF prevented the upregulation of TXNDC5 mRNA in response to TGFβ1 stimulation. (C) Schematic illustration of the mouse Txndc5 promoter luciferase reporter construct, which contains an ATF6 binding site (TGACGTGG, +773∼+780). Deletion of the ATF6 binding site significantly reduced TGFβ1-induced transcriptional activity of the Txndc5 promoter in the absence or presence of TGFβ1. (D) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay showed biotin-labeled Txndc5 promoter probe containing ATF6 binding site was shifted (lane B) when treated with nuclear extract from NIH-3T3 fibroblasts with ectopic ATF6 expression. Unlabeled Txndc5 promoter DNA was used as competitor (lane C) and revealed the specificity of ATF6 binding to Txndc5 promoter. Biotin-labeled Txndc5 promoter probe with ATF6 binding site deletion failed to interact with ATF6 (lane D, E).(#P<0.01, *P<0.001).
