Figure 8. Targeted deletion of Txndc5 protects against isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis and contractile dysfunction.
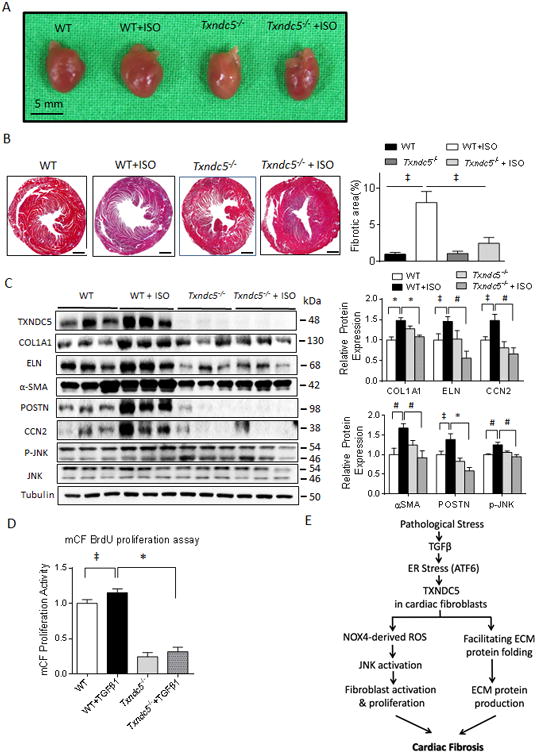
(A) Isoproterenol (ISO, 30 mg/kg/day subcutaneously for 10 days) injection led to marked increase in HW/BW ratio, an indicator of cardiac hypertrophy, in WT, but not in Txndc5-/-, mice. (B) Knockout of Txndc5 attenuated the extent of myocardial fibrosis induced by ISO injection. (C) ISO treatment led to significantly increased fibrogenic proteins (including COL1A1, ELN, CCN2, αSMA, POSTN) and p-JNK expression in WT, but not in Txndc5-/-, mouse LV. (D) Loss of Txndc5 also significantly reduced the proliferation capacity of mCF at baseline and in response to TGFβ1 stimulation. (E) Schematic summary of the proposed profibrotic mechanisms by which TXNDC5 contributes to cardiac fibrosis.(‡P<0.05, #P<0.001, *P<0.001).
