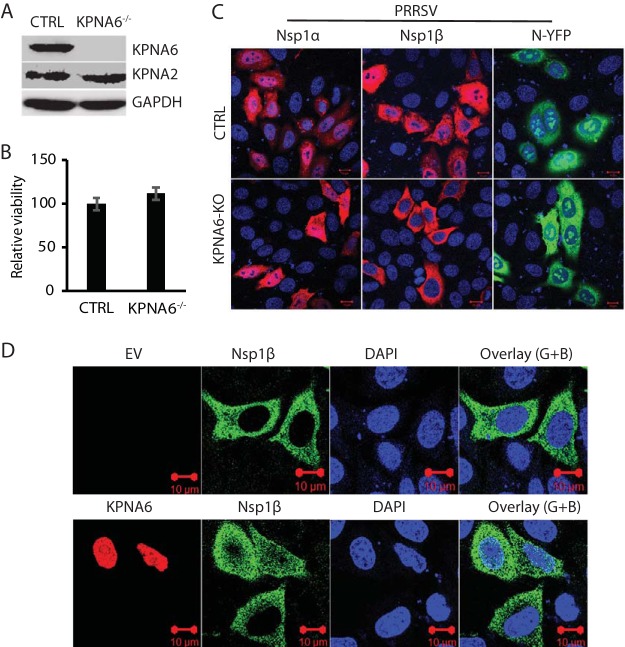
FIG 5.
KPNA6 knockout blocks nuclear translocation of PRRSV nsp1β, whereas exogenous KPNA6 expression restores its nuclear translocation. (A) WB of KPNA6 protein in the KPNA6-knockout HeLa cells. CTRL, control cells stably transfected with empty vector with Cas9; KPNA6−/−, KPNA6-knockout HeLa cells. WB analyses of KPNA6, KPNA2, and GAPDH were conducted. (B) Relative cell viabilities of the KPNA6−/− and CTRL HeLa cells. (C) Confocal microscopy of the KPNA6−/− and CTRL HeLa cells with transient expression of the PRRSV proteins. The cells were transfected with plasmids encoding HA-nsp1α, HA-nsp1β, and N-YFP proteins. IFA with antibody against HA was done. The overlay IFA images show HA-nsp1α and HA-nsp1β in red fluorescence, N-YFP in green fluorescence, and nuclear DNA staining with DAPI in blue. The scale bars in the lower right portion of each image denote 10 μm. (D) Transient exogenous expression of KPNA6 in KPNA6−/− HeLa cells restores the nuclear translocation of PRRSV nsp1β. The cells were transfected with Myc-KPNA6 and HA-nsp1β plasmids. Empty vector (EV) was included as a control. IFA with antibodies against Myc and HA was done. The overlay images of the green and blue channels (“Overlay (G+B)”) are shown. Nuclear DNA was stained with DAPI in blue. The scale bars in the low right portion of each image denote 10 μm.