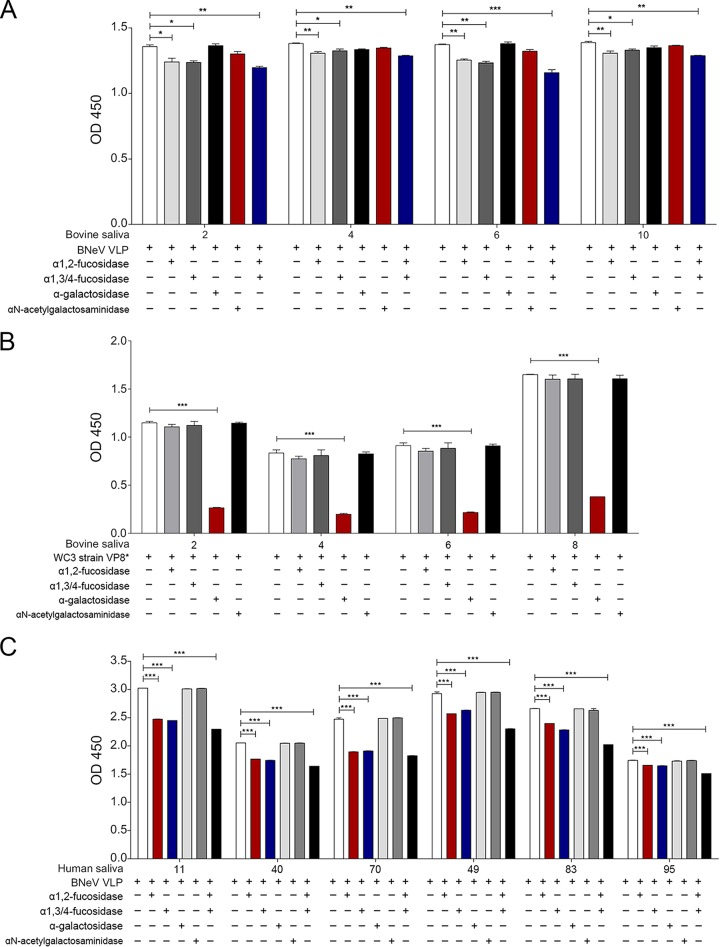
FIG 8.
Blocking of binding of BNeV VLPs and VP8* protein of bovine P[5] strain WC3 to bovine and human saliva samples. (A) Four selected bovine saliva samples expressing either A type (H+/A+/B−) or H type (H+/A−/B−) were coated onto 96-well plates prior to removal of α1,2-linked fucose, α1,3/4-linked fucose, αGal, and GalNAc epitopes from HBGAs by pretreatment with a single specific enzyme or a combination of enzymes. A reduction in the HBGA binding specificity of BNeV VLPs to each bovine saliva sample was determined by saliva-binding assay using hyperimmune serum against BNeV capsid protein as described in Materials and Methods. (B) The GST-VP8* protein of the bovine rotavirus P[5] WC3 strain was used as a positive control. Four bovine saliva samples expressing either A type (H+/A+/B−) or H type (H+/A−/B−) HBGAs were used to remove α1,2-linked fucose, α1,3/4-linked fucose, αGal, and GalNAc epitopes from HBGAs in the saliva samples by individual or combinatorial enzyme pretreatment. A reduction in the HBGA binding specificity of VP8* protein of bovine rotavirus strain WC3 was determined by a saliva-binding assay using hyperimmune serum against VP8* protein. (C) Six human saliva samples expressing either A type (H+/A+/B−) or H type (H+/A−/B−) were used to remove α1,2-linked fucose, α1,3/4-linked fucose, αGal, and GalNAc epitopes from HBGAs in the saliva samples by pretreatment with each specific enzyme individually or in various combinations. Reduction in the HBGA binding specificity of BNeV VLPs was determined by a saliva-binding assay using hyperimmune serum against BNeV capsid protein as described in Materials and Methods. Blocking of BNeV VLPs to each sample was visualized using TMB and measured at 450 nm in three independent experiments. Error bars indicate SD from triplicate samples.