Fig. 2.
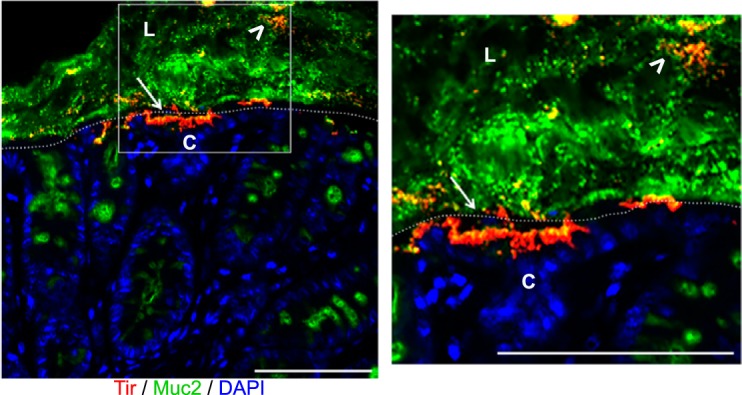
Citrobacter rodentium localizes within the mucus layer and on the apical surface of the intestinal epithelium. Immunofluorescent staining of colonic tissue from a C57BL/6 mouse, 6 days post-C. rodentium infection. Antibodies were used against the translocated intimin receptor (Tir; red) to identify C. rodentium, mucus (Muc2; green), and DNA [4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI); blue]. During infection, C. rodentium is found within the intestinal mucus layer (white arrowheads), as well as infecting the apical surface of the intestinal epithelium (white arrows). L, lumen; C, crypts, tissue surface, dotted, white lines. Original scale bars, 50 μm.
