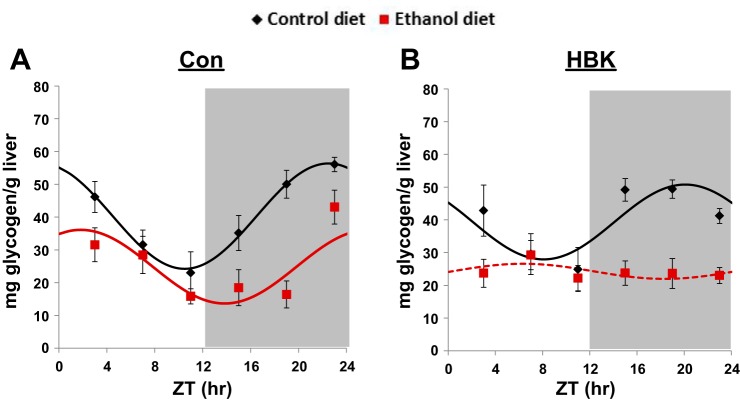
Fig. 3.
Effect of chronic alcohol consumption and hepatocyte-specific Bmal1 gene deletion on hepatic glycogen content. Male hepatocyte-specific BMAL1 knockout (HBK) and control genotype (Con) littermates, 8 wk of age, were fed a control or alcohol-containing liquid diet for 5 wk. Livers were collected every 4 h at ZT 3, 7, 11, 15, 19, and 23 (ZT 0: lights on; ZT 12: lights off, gray shading). A and B: hepatic glycogen content for Con and HBK mice, respectively. Data were fitted to a cosine function and are expressed as means ± SE for n = 5–8 mice/genotype/diet/time point. Solid lines indicate a significant cosine fit, whereas dashed lines indicate a nonsignificant fit. Results for ANOVA and Cosinor analyses are provided in Tables 3 and 4, respectively.