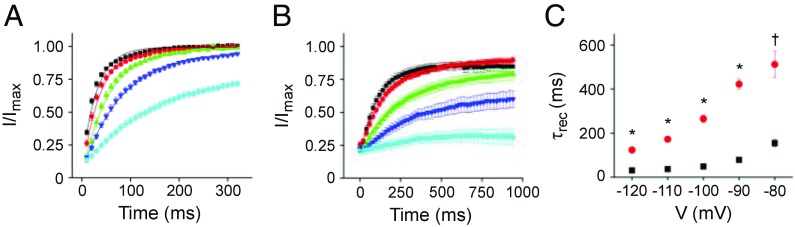
Fig. 6.
V404M significantly slows recovery from inactivation. (A) Wild-type and (B) V404M channels were maximally inactivated from the closed state by pulsing to −40 mV (the wild type) for 500 ms or −60 mV (V404M) for 1 s before repolarizing for various durations to recovery voltages from −120 to −80 mV (−80 mV, cyan; −90 mV, blue; −100 mV, green; −110 mV, red; −120 mV, black). Remaining peak current amplitude was measured in a subsequent test pulse to +60 mV, normalized to the maximum peak current amplitude at +60 mV, and plotted vs. recovery time. Data, shown as mean ± SEM, were fitted with a single exponential function to estimate τrec. Fits (solid curves) are shown superimposed on the data. (C) Values of τrec for the wild type (■; n = 5) and V404M (red ●; n = 8) have been plotted vs. recovery voltage. Values of τrec differed significantly at every voltage. *P < 0.00001; †P < 0.0005.