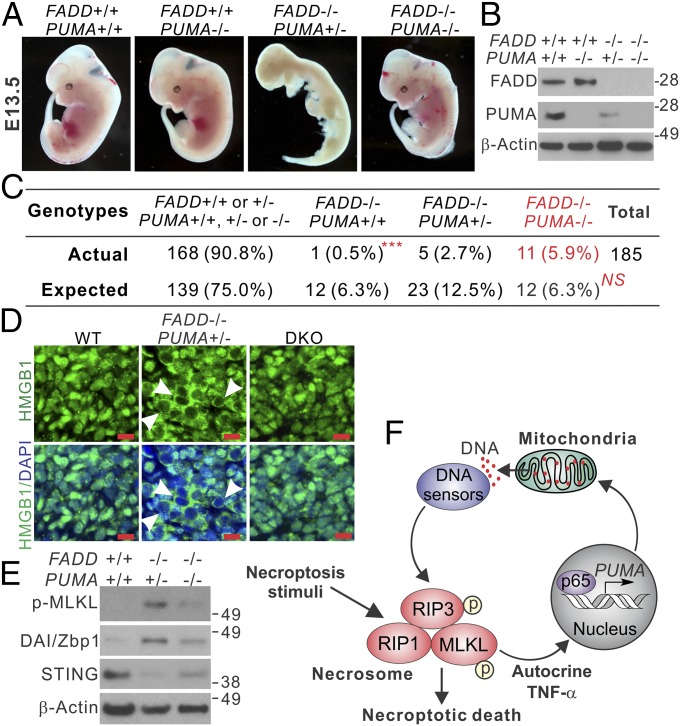
Fig. 6.
PUMA deficiency rescues defective embryonic development and suppresses necroptosis in FADD KO embryos. (A) Representative pictures of mouse embryos with indicated FADD and PUMA genotypes at 13.5 d (E13.5). (B) Western blots of FADD and PUMA in E13.5 embryos with the indicated genotypes. (C) Expected and observed numbers of embryos with the indicated FADD and PUMA genotypes from 185 dissected E13.5 embryos. ***P < 0.001, FADD−/−/PUMA−/− vs. FADD−/−/PUMA+/+; NS, P = 0.5252, FADD−/−/PUMA−/− vs. the expected ratio of Mendelian inheritance (χ2 test). (D) HMGB1 staining of fibroblast tissues from E13.5 embryos with the indicated genotypes. Arrowheads indicate cells with cytoplasmic HMGB1 staining and hollow nuclei. (Scale bars: 10 μm.) (E) Western blots of indicated proteins in E13.5 embryos with the indicated genotypes. (F) Model depicting the role of PUMA in necroptosis.