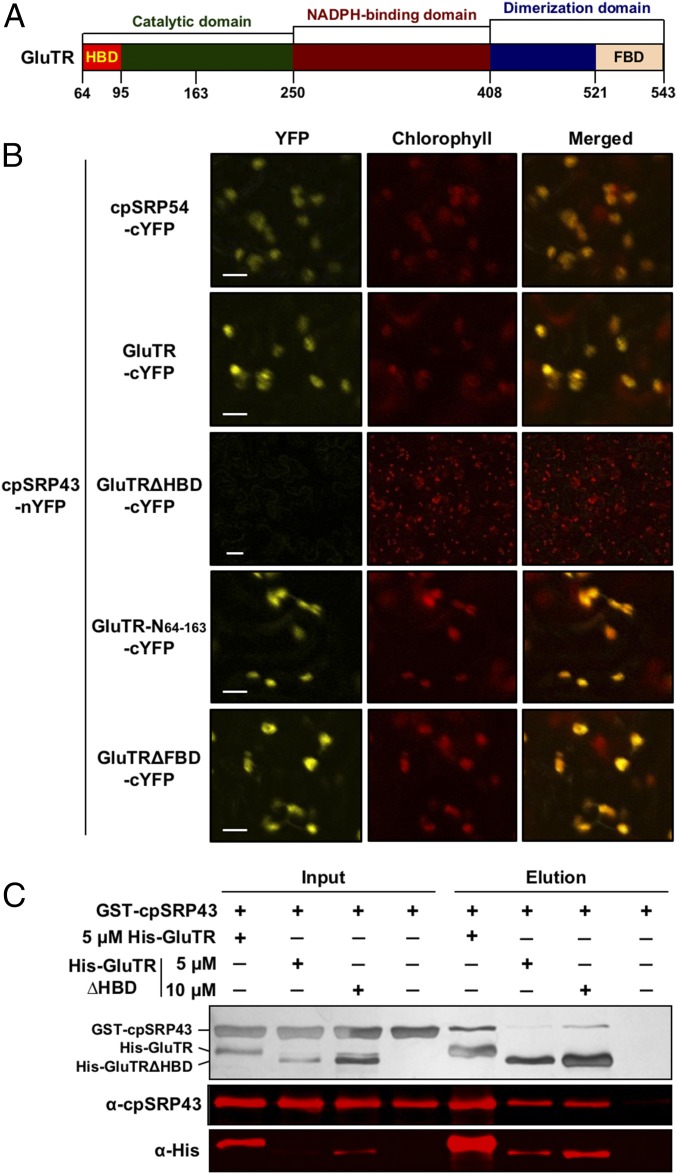
Fig. 6.
cpSRP43 interacts with the N-terminal part of GluTR. (A) Schematic overview of GluTR domains. (B) BiFC assay reveals that cpSRP43 interacts with the N-terminal HBD of GluTR. The cpSRP43 fused to nYFP and cpSRP54/GluTR variants fused to cYFP were expressed in N. benthamiana following Agrobacterium infiltration and analyzed by confocal microscopy 3 d after infiltration. The cpSRP54 was used as a positive control. (Scale bars: 10 μm.) (C) Deletion of HBD in GluTR weakens the binding to cpSRP43, as shown by the in vitro His pull-down assay. Indicated concentrations of recombinant purified WT His-GluTR or His-GluTRΔHBD were used as bait and incubated with 10 μM GST-cpSRP43. Input and elution fractions were stained with silver (Upper), blotted, and probed with the indicated antibodies (Middle and Lower).