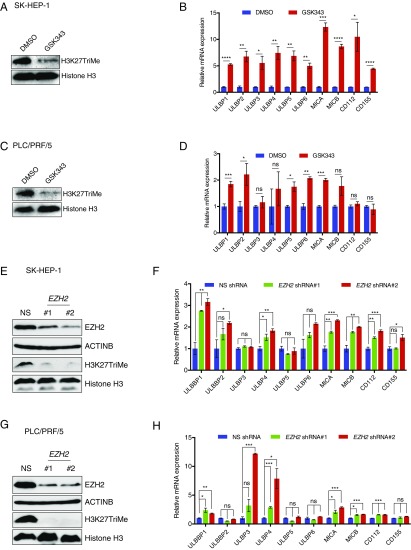
Fig. 3.
Pharmacological and genetic inhibition of EZH2 results in the up-regulation of NK cell ligands on HCC cells. (A) SK-HEP-1 cells were treated with DMSO or the EZH2 inhibitor GSK343 (3 μM) for 48 h. Immunoblotting for the EZH2-mediated H3K27TriMe mark was performed using DMSO or GSK343-treated cells. Histone H3 was used as a loading control. (B) SK-HEP-1 cells were treated with DMSO or the EZH2 inhibitor GSK343 (3 μM) for 48 h. NK cell ligand mRNA expression in GSK343-treated cells relative to DMSO-treated cells is shown. (C) PLC/PRF/5 cells were treated with DMSO or the EZH2 inhibitor GSK343 (3 μM) for 48 h. Immunoblotting for the EZH2-mediated H3K27TriMe mark was performed using DMSO- or GSK343-treated cells. Histone H3 was used as a loading control. (D) PLC/PRF/5 cells were treated with DMSO or the EZH2 inhibitor GSK343 (3 μM) for 48 h. NK cell ligand mRNA expression in GSK343-treated cells relative to DMSO-treated cells is shown. (E) SK-HEP-1 cells expressing either a nonsilencing (NS) shRNA or EZH2 shRNAs were analyzed for the indicated proteins by immunoblotting. (F) SK-HEP-1 cells expressing either a NS shRNA or EZH2 shRNAs were analyzed for the indicated ligands by RT-qPCR. NK cell ligand mRNA expression is plotted relative to NS shRNA-expressing cells. (G) PLC/PRF/5 cells expressing either a NS shRNA or EZH2 shRNAs were analyzed for the indicated proteins by immunoblotting. (H) PLC/PRF/5 cells expressing either a NS shRNA or EZH2 shRNAs were analyzed for the expression of the indicated ligands by RT-qPCR. NK cell ligand mRNA expression is plotted relative to NS shRNA-expressing cells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; and ****P < 0.0001.