Figure 2.
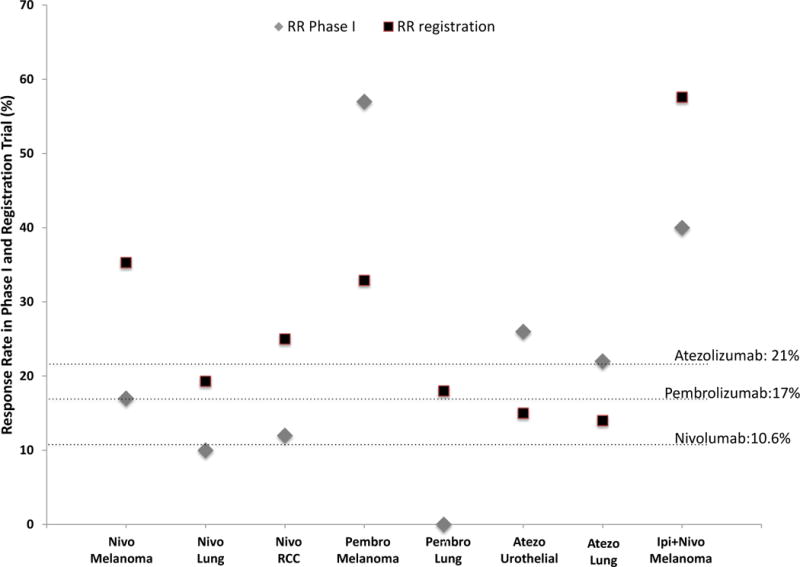
Correlation between the response rate (%) in a particular tumor included during the phase I trial (gray rhombus) and the later registration trial (black square). Horizontal axis depicts the immune checkpoint inhibitor in each approved indication. Response rate information for phase I was only included if a metastatic tumor of the same histology from the approval was tested. Dashed lines represent the overall response rate in the phase I trial (including all tumor types treated).
The figure shows that the response rates in later trials were generally higher than in the phase I trials; however, in the cases of pembrolizumab in melanoma and atezolizumab in urothelial and lung cancer, response rates in phase I trials were higher than in later trials. Some approvals were excluded as the phase I did not included the tumor types (Nivolumab for Hodgkin lymphoma and HNSCC; Pembrolizumab for Hodgkin Lymphoma, HNSCC, urothelial cancer and MSI-H tumors; Avelumab for Merkel Cell Carcinoma and urothelial cancer and Durvalumab for urothelial cancer).
Abbreviations: atezo = atezolizumab; ipi = ipilumumab; nivo = nivolumab; pembro = pembrolizumab; MSI-H: microsatellite instability high cancers; RCC = renal cell cancer: RR = response rate
