Figure 6. Vxn is required for retinal neuron differentiation.
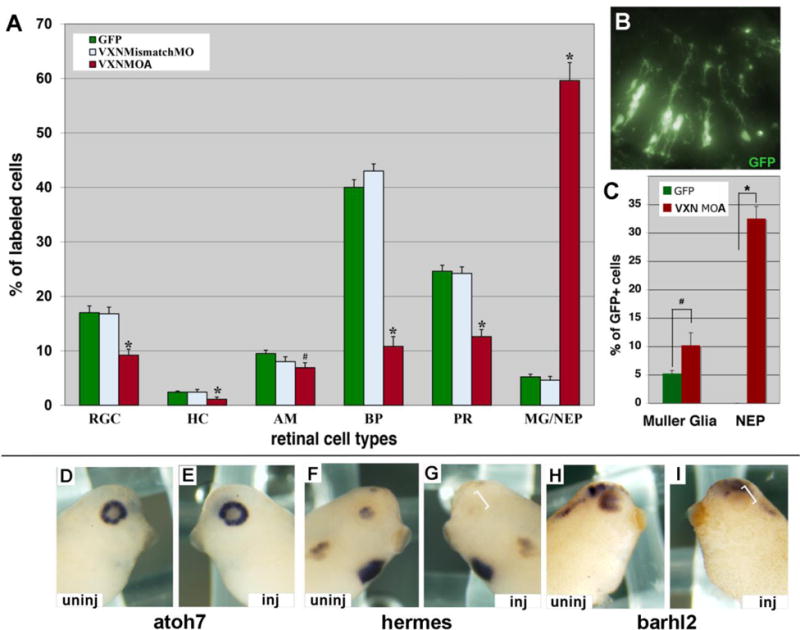
(A-C) mRNA for GFP (300pg) was injected alone or together with 3ng of vxn mismatch MO-A or vxn MO-A into 1 dorsal blastomere at the 32-cell stage. Embryos were cryosectioned at stage 41, and GFP-labeled retinal cell types were counted. vxn MO-A caused a significant decrease in all retinal neuron types, and a significant increase in Muller glia (MG) and/or neuroepithelial cells (NEP) (A). A section of stage 41 retina showing many GFP-labeled retinal cells with the morphology of Muller glia and/or NEPs (B). Immunostaining for CRALBP to distinguish MG from NEPs showed that both populations increased significantly (C).
(D-I) Injection of 20ng of vxn MO-B at 8CS did not alter atoh7 expression in stage 34-35 embryos (D,E), but prevented expression of hermes (F,G) and barhl2 (H,I) on the injected (inj) side (brackets; E,G,I) when compared to the uninjected (uninj) side (D, F, H).
RGC, retinal ganglion cells; HC, horizontal cells; AC, amacrine cells; BP, bipolar cells; PR, photoreceptor cells; MG, Muller glial cells; NEP, neuroepithelial cells. *p<0.001 and #p<0.01 by Student’s t-test.
